들깻잎 중 Afidopyropen, Pydiflumetofen 및 Mefentrifluconazole의 잔류특성 및 위해성 평가
 ; Byung Jin Bae ; Sang Won Woo ; Hye Jin Jeong ; You Jin Jang ; Jong Woo Park ; Seok Chai*
; Byung Jin Bae ; Sang Won Woo ; Hye Jin Jeong ; You Jin Jang ; Jong Woo Park ; Seok Chai* ; Kun Sik Lee ; Young Soo Keum1 ; Kee Sung Kyung2 ; Jang Eok Kim3 ; Tae Hwa Kim
; Kun Sik Lee ; Young Soo Keum1 ; Kee Sung Kyung2 ; Jang Eok Kim3 ; Tae Hwa Kim
초록
본 연구는 소면적 재배작물인 들깻잎 중 afidopyropen, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole의 경시적 잔류특성과 위해성을 평가하기 위하여 수행되었다. 시험 약제는 살포횟수를 달리하여 살충제는 7일 간격으로 2회, 살균제는 3회 살포하였다. 경시적 잔류양상을 평가하기 위한 들깻잎 시료는 최종약제살포 후 0, 1, 3, 5, 7 및 10일차에 각각 수확하여 분석하였다. 들깻잎 중 시험 농약의 정량한계는 모두 0.01 mg/kg이었으며, Afidopyropen, 및 대사체 M440I007, pydiflumetofen, mefentrifluconazole의 회수율 결과는 67.2-114.8%의 범위로 양호하였다. 들깻잎 중 afidopyropen의 잔류량은 0.06-0.42 mg/kg으로 상대적으로 잔류량이 낮은 경향을 보였고, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole의 잔류량은 12.22-28.90 mg/kg 및 2.35-6.09 mg/kg으로 상대적으로 높은 잔류량을 보였으며, 이는 농약의 특성보다는 살포횟수와 실질적으로 살포된 유효함량에 가장 큰 영향을 받은 것으로 판단되었다. First order kinetics model의 반감기 산출 공식에 적용한 결과, 들깻잎 중 afidopyropen의 반감기는 4 .2일이었고, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole의 반감기는 각각 8.7일과 8.3일로 상대적으로 afidopyropen의 반감기가 짧은 것은 수중광분해 반감기가 6-19.3일로 짧은 영향인 것으로 사료된다. 들깻잎에 살포된 afidopyropen은 pydiflumetofen과 mefentrifluconazole의 잔류량은 모두 경시적으로 감소하는 경향을 보였으며, 일일섭취허용량 대비 일일섭취추정량은 모두 1.5% 미만으로 안전한 수준으로 나타났다.
Abstract
This study was carried out to evaluate the residual patterns and dissipation of afidopyropen, pydiflumetofen and mefentrifluconazole in perilla leaf. Perilla (Perilla frutescens) leaf was applied twice with afidopyropen or three times with pydiflumetofen or mefentrifluconazole. All pesticides were 2,000 times dilluted in water, and each application was made at interval of 7 days. Perilla leaf samples were harvested 0, 1, 3, 5, 7 and 10 days after final application and used for pesticide residue analysis. Recoveries of all tested pesticides in perilla leaf were good in the range of 67.2% to 114.8%. Residual amounts of afidopyropen (0.06-0.42 mg/kg) were lower than those of pydiflumetofen (12.22-28.90 mg/kg) and mefentrifluconazole (2.35-6.09 mg/kg). Based on first-order kinetics model, half-lives of afidopyropen were 4.2 days, and those of pydiflumetofen and mefentrifluconazole were 4.2, 8.7 and 8.3 days, respectively, indicated longer half-lives compared to afidopyropen. Residual amounts of the three pesticides sprayed on perilla leaves tended to decrease according to the harvest date, and Residual amounts and half-lives of the apidopyrofen was lower and shorter than pydiflumetofen and mefentrifluconazole. Also, ratio of the estimated daily intake compared to the acceptable daily intake was less than 1.5%, representing safe level for all tested pesticides.
Keywords:
Half-life, minor crop, Perilla leaf, pesticide residue, risk assessment키워드:
반감기, 소면적 재배작물, 들깻잎, 잔류농약, 위해성 평가서 론
농약의 사용은 작물로부터 다양하게 발생하는 각종 병해충을 방제하여 최종 농산물의 생산성을 증가시켰지만 사용된 농약의 일부가 농산물에 잔류하여 최종 소비자에 대한 안전성 문제를 발생시킬 수 있다. 농산물에 대한 농약의 안전성을 확보하기 위하여 우리나라는 작물별 농약 잔류허용기준(Maximin Residue Levels, MRLs) 및 안전사용기준을 설정하고 있다. 이러한 기준들을 설정하기 위하여 작물 중 농약의 잔류시험 결과와 약효, 약해 및 독성 시험의 결과가 종합적으로 활용된다. 우리나라는 2019년부터 농약허용물 질목록고시제(Positive List System, PLS)를 전면시행하여 잔류허용기준 미설정 농약에 대한 잔류허용기준을 0.01 mg/kg으로 일괄 적용하여 관리하고 있다(MFDS, 2022). 이에 따라 잔류허용기준 미설정 농약의 등록이 시급한 실정이나 소면적 작물은 재배면적이 1,000 ha 미만으로 작고 농약의 사용량도 적어 농약 회사들이 농약 등록에 미온적으로 잔류허용기준이 설정된 농약의 수가 제한적이다(Lee, 2013).
들깻잎은 소면적 작물로 재배면적은 전국에 약 900 ha이며 단위면적당 소득이 높고, 외식문화의 증가로 인한 소비의 증가로 전국 각지에서 재배면적이 늘어나고 있다(RDA, 2018). 2021년 농산물품질관리원의 농산물 잔류농약 분석결과에 따르면 2021년 8월 기준으로 용도변경, 출하연기 또는 폐기처분 등의 조치를 받은 부적합 건수가 279건이었으며, 전체 분석건수 28,550건 중 약 1.0%의 부적합 비율을 보였다(NAQS, 2021). 이 중 들깻잎의 부적합 건수는 15건으로 깻잎 분석 건수 409건 중 부적합 비율은 약 3.7%에 달하였다. 들깻잎을 포함한 상추, 부추, 시금치 등 엽경채류는 분석 건수 대비 부적합 비율이 가장 높은 것으로 나타났다(NAQS, 2021). 따라서 들깻잎과 같은 소면적 엽경채류 재배작물의 농약 등록 및 잔류허용기준 및 위해성에 대한 연구가 더욱 필요 할 것으로 사료된다.
Afidopyropen은 Pyropene계 신규 살충제로 Meiji Seika Pharma사와 BASF사가 공동 개발한 농약으로(Jeanmart, 2016) 진딧물, 온실가루이, 총채벌레 등 흡즙성 해충에 우수한 효과를 보인다. 이 농약은 주로 과수류, 채소류, 목화 등에 발생하는 해충 방제에 사용되며, 아직 밝혀지지 않은 독특한 작용기작으로 진딧물에 높은 효과를 나타낸다고 보고하고 있다(Leichter et al., 2013). 또한, 작물에서 afidopyropen의 대사체 M440I007은 모화합물의 23-91% 수준으로 생성되며, 모화합물 수준의 독성을 보여 afidopyropen과 함께 합산하여 잔류량을 평가하고 있다(JMPR report, 2019). Pydiflumetofen는 Syngenta사에서 개발한 Pyrazole Caboxamide계 살균제로 작물에 발생하는 흰가루병, 잿빛곰팡이병 등에 우수한 효과를 보이는 신규 약제이다. Pydiflumetofen은 식물 병원균의 호흡을 저해(Succinate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors (SDHI))하는 작용기작을 가지고 있으며(Avenot and Michailides, 2010), 기존의 살균제보다 효과가 우수하여 전 세계적으로 두류, 과일, 과채류 및 곡류 등 다양한 작물에 등록되어 사용된다. 국내에도 사용가능 작물의 범위를 넓히고 있어 더 많은 작물에 대한 연구가 필요한 실정이다(Noh et al., 2019). Mefentrifluconazole은 BASF사에서 개발한 신규 triazole계 침투성 살균제이다. 이 농약은 살포된 성분이 잎으로 흡수되어 증산작용에 의해 선단조직으로 이행되면서 식물체 표면과 조직 내부 모두에 잔류하여 약효를 나타내게 되며, 검은별무늬병, 균핵병, 흰가루병 등에 방제효과를 보인다(Park et al., 2020). 현재 afidopyropen, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole은 미국, 일본 등 해외에서 적용범위가 소면적 작물에 확대되고 사용량이 점차 증가하는 것에 비해 국내에서는 이러한 농약들의 소면적 작물에 대한 안전성 연구가 미흡하여 농약잔류허용기준 및 안전사용기준 설정을 위한 잔류시험 결과 확보가 시급한 실정이다.
들깻잎에 대한 재배기간 동안의 시험 농약의 초기 잔류량 및 잔류농약의 반감기 반감기를(half-life)를 계산하여 시험 농약의 잔류특성을 구명하는 것은 최종 생산된 농산물에 대한 위해성 평가를 하기 위해 중요하다. 농약의 잔류특성을 예측하기 위한 다양한 방식들이 연구되었으나(Park et al., 2005; Fantke and Juraske, 2013), 최근에 보편적으로 사용하는 방식은 first order k inetics model을 사용하여 해석하고 있으며 이를 통하여 농약의 잔류량이 예측이 가능할 것으로 사료된다(Kim et al., 2012).
본 연구는 소면적 재배작물인 들깻잎에 대한 신규농약 afidopyropen, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole 3종에 대하여 국내 잔류허용기준 설정을 위한 자료로 사용하기 위해 경시적 잔류특성을 조사하였으며, first order kinetics model을 적용하여 각 농약의 소실반감기를 산출하여 잔류허용기준의 설정 근거를 제시하고, 위해성을 평가하기 위하여 수행하였다.
재료 및 방법
시험약제
들깻잎의 잔류특성을 구명하기 위하여 선정한 농약 afidopyropen (purity 94.52%), pydiflumetofen (purity 99.1%) 및 mefentrifluconazole (purity 99.26%)의 표준품은 Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH (Augsbug, Germany)의 제품을 구입하여 사용하였고, afidopyropen의 대사체 M440I007의 표준품(purity 89.9%)은 BASF (Ludwigshafen, Germany)의 제품을 구입하여 사용하였다. 시험에 사용된 농약은 아피도피로펜 2.5% 미탁제(상표명: 베르시스), 피디플루메토펜 18.35% 액상수화제(상표명: 미래빛) 및 메펜트리플루코나졸 10% 액상수화제(상표명 : 레빅사)를 사용하였다. 제품농약의 안전사용기준은 Table 1에 제시하였다.
시험작물 및 약제살포
시험 작물인 들깻잎의 품종은 ‘남천일호’이며, 경상북도 경산시 하양읍에 위치한 포장에서 시설재배 하였다. 처리구는 반복구당 2m× 5m (10m2)로 설정하였고, 재식간격은 10 cm × 10 cm였다. 약제살포는 전기충전식 분무기(모델명: MSB1015Li, 마루야마)를 이용하여 2,000배 희석액을 7일 간격으로 살충제인 afidopyropen은 2회, 살균제인 pydiflumetofen과 mefentrifluconazole은 3회 처리하였다. 시료의 채취는 처리구당 3반복으로 반복 당 500 g 이상 채취하였으며, 최종약제살포 후 0, 1, 3, 5, 7 및 10일 간격으로 수확하였다. 수확한 시료는 드라이아이스와 함께 균질화하여 -20oC에서 냉동보관하였다.
시약 및 용매
잔류농약 분석에 사용한 용매인 acetonitrile은 J.T. Baker Chemical Co. (USA)에서, sodium chloride 및 sodium sulfate는 Junsei Chemical Co. (Japan)에서, formic acid 및 dichloromethane은 Duksan pure chemicals (Korea)에서, 초순수는 Fisher Scientific Korea Ltd. (USA)에서, 정제에 사용한 PSA 및 C18은 Agilent (USA)에서 구입하여 사용하였다.
잔류농약 분석
들깻잎 중 afidopyropen, M440I007 및 pydiflumetofen의 잔류농약 분석은 QuEChERS 방법을 변형하여 적용하였다. 시료를 각각 10g씩 칭량한 후에 acetonitrile 20 mL와 sodium chloride 2 g을 첨가하여 30분간 진탕·추출하였다. 추출 후 3,500rpm에서 5분간 원심분리하여 상등액을 syringe filter (0.2 μm)로 여과한 후 LC-MS/MS에 5 μL씩 주입하였다. Mefentrifluconazole의 경우, 10 g의 시료에 acetone 60 mL를 첨가하고 homogenizer를 이용하여 10,000 rpm으로 5분간 고속마쇄·추출하여 추출물을 celite 545가 깔린 büchner funnel상에서 감압·여과하고 30 mL의 acetone으로 용기 및 잔사를 씻어 앞의 여액과 합하였다. 이 여액을 separatory funnel에 옮겨 증류수 150mL와 포화식염수 50 mL를 가하고 dichloromethane 50 mL로 2회 분배한 후 anhydrous sodium sulfate층에서 탈수하고 40oC 수욕조상에서 감압·농축하였다. 농축 후 잔사를 acetonitrile 10 mL에 재용해하여 분석시료로 사용하였다. 시료의 정제를 위해 50 mg의 PSA 및 C18이 담긴 micro tube에 분석시료 1mL를 넣고 진탕·혼화한 후 10,000 rpm에서 3분간 원심분리하고 상등액을 syringe filter (0.2 μm)로 여과하여 LC-MS/MS에 2 μL씩 주입하였다. 정량분석을 위한 각 농약의 표준검량선은 각 표준품을 무처리 시료로 희석하여 afidopyropen 및 pydiflumetofen은 0.002, 0.005, 0.01, 0.02, 0.05, 0.08 및 0.1 mg/L의 calibration solution을 조제하여 각각 5 uL씩 주입하였고, mefentrifluconazole은 0.005, 0.01, 0.02, 0.05, 0.1 및 0.2mg/L의 calibration solution을 조제하여 각각 2 uL 씩 주입하였다. 기기분석조건은 Table 2 및 3에 나타내었다.
회수율 시험
회수율 시험은 무처리 들깻잎 시료에 시험 농약의 표준용액을 정량한계(limit of quantitation, LOQ), 정량한계의 10배 및 시료의 최고 잔류농도 수준이 되도록 처리하여 상기분석법과 동일한 방법으로 수준별 5반복 분석하였으며, 정량한계는 아래의 식을 이용하여 산출하였다.
생물학적 반감기 및 감소상수
들깻잎 중 afidopyropen (대사체 M440I007의 합), pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole의 반감기(T)는 농약의 초기 잔류량(C0), 경과일수(t), 감소상수(k) 및 t시간 경과 후 농약의 잔류량(Ct)을 아래의 first order kinetics model에 대입한 감소식에 따라 산출하였다.
위해성 평가
들깻잎 중 afidopyropen, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole의 안전성 평가를 위하여 일일섭취허용량(acceptable daily intake, ADI) 대비 일일섭취추정량(estimated daily intake, EDI)인 %ADI로 평가하였다(Jin, 2018). 들깻잎의 일일섭취량인 0.0025 kg을 최대 잔류량과 곱한 후 한국인의 평균 체중으로 나누어 일일섭취추정량을 산출하였다(KHIDI, 2022).
| (3) |
결과 및 고찰
정량한계 및 회수율
들깻잎 중 afidopyropen, 대사체 M440I007, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole 분석법의 정량한계는 모두 0.01mg/kg이었으며, 회수율은 72.7-107.9%로 나타났다. 이는 작물 잔류성 시험의 기준인 회수율 범위 70-120%를 나타내어 잔류농약 분석법 기준을 만족하였다(Table 4).
들깻잎 수확일에 따른 잔류량 변화
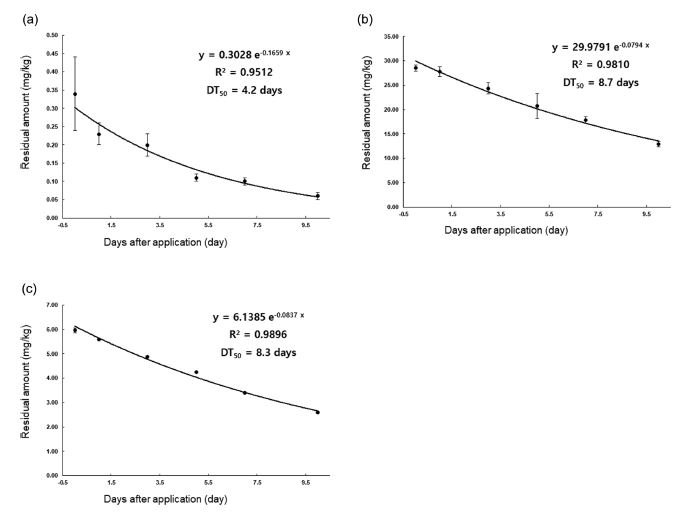
들깻잎의 최종 약제 살포 후 경과일에 따른 afidopyropen, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole의 잔류농도 변화는 Table 5에 나타내었다. 들깻잎 중 afidopyropen의 초기 잔류량은 0 .34 ± 0.10mg/k g이었고, 최종약제 살포 7일 및 10일 경과 후 잔류량은 각각 0.10 ± 0.01 mg/kg 및 0.06±0.01 mg/kg으로 초기 잔류량 대비 각각 약 70% 및 82% 감소하였다. Pydiflumetofen의 경우 초기 잔류량은 28.52±0.59 mg/kg이었고, 7일 및 10일 경과 후 잔류량은 각각 17.83 ± 0.64 mg/kg 및 12.90 ± 0.59 mg/kg으로 초기 잔류량에서 약 36% 및 54% 감소한 수치를 보였다. 또한, mefentrifluconazole의 초기 잔류량은 5 .96 ± 0.13mg/k g으로 나타났으며, 7일 및 10일 경과 후의 잔류량 결과는 각각 3.39 ± 0.44 및 2.59 ± 0.22 mg/kg이었고, 이는 초기 잔류량의 결과에서 각각 43% 및 57% 감소한 결과를 나타내었다(Table 5). Lee 등(2008)의 연구에 따르면 들깻잎과 같이 단기간에 성장이 빠른 작물의 경우 작물 중 잔류농약의 반감기에 영향을 미치는 가장 큰 요인은 작물의 비대성장으로 보고하였다. 본 연구의 잔류량의 소실 또한 각 농약의 특성보다는 작물의 비대성장이 가장 큰 요인으로 작용한 것으로 사료된다. 또한, Afidopyropen의 초기 잔류량이 pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole 보다 상대적으로 낮은 잔류양상을 나타내고 있으며 이는 시험농약의 실질적인 유효함량에 영향을 받은 것으로 사료된다.
Afidopyropen, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole의 다른 작물에서 잔류허용기준을 보면 딸기의 경우는 각각 0.2, 2.0, 1.0 mg/kg이었고 피망의 경우 각각 0.07, 2.0, 1.0 mg/kg이었다(MFDS, 2022). Ripley 등(2003)에 따르면 들깻잎과 같은 엽채류의 경우 부피에 대한 노출된 표면적이 넓기 때문에 잔류량이 높은 특성을 보인다고 보고되었다.
생물학적 반감기 및 감소상수
시험기간 중 들깻잎 중 잔류하는 각 농약에 대한 감소회귀식은 f irst o rder k inetics model의 반감기 산출 공식에 적용하여 계산하였다. Afidopyropen은 y=0.3028e-0.1659x(R2=0.9512), pydiflumetofen은 y=29.9791e-0.0794x(R2=0.9810), mefentrifluconazole은 y=6.1385e-0.0837x(R2=0.9896)와 같은 식을 얻을 수 있었고(Fig. 1), 각각의 식을 이용하여 반감기를 산출한 결과 각각 4.2일, 8.7일, 8.3일로 나타났다. Chen 등(2018)의 연구에서 afidopyropen의 밀 작물에 대한 반감기를 1.65일이라고 보고하였고, Xie 등(2019)의 연구에서는 오이 및 복숭아에서 afidopyropen의 초기 반감기는 1.1일 및 2.0일이라고 밝혔다. Pydiflumetofen은 이전 연구에서 2년동안 4개 지역의 논에서 실험한 결과 볏짚에서의 반감기는 1.09-9.34일이라고 보고된 바 있으며(Bian et al., 2021), mefentrifluconazole의 반감기 연구에서는 오이에서 약 4.0일의 반감기를 가진다는 연구결과가 보고되었다(Li et al., 2021). 본 연구에서도 이전의 연구결과와 유사하게 afidopyropen의 반감기가 pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole에 비해 상대적으로 빠른 것으로 나타났으며, 시험농약의 물리화학적 특성을 보면 수중광분해의 반감기가 afidopyropen은 6-19.3일, pydiflumetofen은 95.3일, mefentrifluconazole은 313일로 알려져 있다(MDA, 2022). Afidopyropen의 반감기가 상대적으로 빠른 것은 시험농약의 물리화학적 특성인 광분해 영향으로 판단되었다.
안전성 평가
들깻잎에 대한 afidopyropen, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole의 안전성을 평가하기 위해 일일섭취허용량과 일일섭취추정량으로 %ADI를 산출하였다. 각 농약의 %ADI는 afidopyropen은 0.00-0.02%으로 매우 낮은 수준으로 확인되었고, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole은 각각 0.60-1.31%, 0.33-0.73%로 확인되었다(Table 6). pydiflumetofen과 mefentrifluconazole의 %ADI는 afidopyropen에 비하여 높은 수치를 보였지만, FAO/WHO에서 %ADI가 10% 미만인 경우 잔류농약 위험성이 낮다고 보고되고 있으며(Lee, 2019), 시험 농약의 최대 잔류량을 기준으로 하여도 각 농약 모두 1.5% 미만으로 나타났기 때문에 안전한 것으로 판단된다.
들깻잎은 조리하지 않은 생야채나 고추와 젓갈 등의 양념재료를 사용한 절임 가공법이 가장 선호도가 높은 섭취방법인데, 들깻잎과 같은 엽채류의 경우 데쳐먹는 등의 조리·가공과정을 거지거나 세척과정을 거치면 잔류농약을 크게 감소시킬 수 있다고 보고된 바 있다(Choi et al, 2000; Cung et al, 2010; Kwon et al, 2009). 따라서 세척과정과 조리과정을 거친 들깻잎의 경우 afidopyropen, pydiflumetofen 및 mefentrifluconazole의 실질적 식이 섭취 단계에서는 더욱 안전할 것으로 판단되었다.
본 연구에서 afidopyropen, pydiflumetofen 및 mfentrifluconazole의 잔류특성 및 반감기 결과를 토대로 안전사용기준 및 잔류허용기준 설정에 대한 자료로 충분히 활용될 수 있을 것으로 보이며 %ADI가 1.5% 이하로 재배 작물의 안전성을 충분히 확보한 것으로 사료된다.
Acknowledgments
이 논문은 식품의약품안전처 연구사업(00-21-8-032000)의 지원을 받아 수행되었으며, 이에 감사드립니다.
이해상충관계
저자는 이해상충관계가 없음을 선언합니다.
References
-
Avenot HF, Michailides TJ, 2010. Progress in understanding molecular mechanisms and evolution of resistance to succinate dehydrogenase inhibiting (SDHI) fungicides in phytopathogenic. fungi. Crop Prot. 29(7):643-651.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2010.02.019]

-
Bian C, Luo J, Gao M., Shi X, Li Y, et al., 2021. Pydiflumetofen in paddy field environments: Its dissipation dynamics and dietary risk. Microchemical Journal. 170: 106709.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106709]

-
Chen Y, Guo M, Liu X, Xu J, Dong F, et al., 2018. Determination and dissipation of afidopyropen and its metabolite in wheat and soil using QuEChERS–UHPLC–MS/MS. J Sep Sci. 41(7):1674-1681
[https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201700773]

- Choi YH, Han JS, 2000. A Survey on Perilla Leaves Uses. J. East Asian Soc. Dietary Life 10(5):445-454.
- Chung HJ, Cheon HS, 2010. Consumption and Preference of Korean Perilla Leaves (Perilla fructescens var. japonica hara) by Daejeon Area Consumers. J East Asian Soc Dietary Life 20(2):193-200.
-
Fantke P, Juraske R, 2013. Variability of pesticide dissipation half-lives in plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(8):3548-3562.
[https://doi.org/10.1021/es303525x]

-
Jeanmart S, Edmunds AJ, Lamberth C, Pouliot M, 2016. Synthetic approaches to the 2010-2014 new agrochemicals. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 24(3):317-341.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2015.12.014]

-
Jin MJ, Park HK, Jeong HR, Lee JW, Jo SH, et al., 2018. Residual Characteristics and safety Assessments of the Fungicide Fenhexamid in some Minor Crops. Korean J. Pestic. Sci. 22(4):363-369.
[https://doi.org/10.7585/kjps.2018.22.4.363]

- JMPR report, 2019. Pesticide residues in food 2019 : 31-73 (Afidopyropen). Joint Meeting of the FAO Panel of Experts on Pesticide Residues, Rome.
- KHIDI, 2022. National nutrition statistics_food intake. https://www.khidi.or.kr, (Accessed Feb. 14. 2022).
-
Kim JH, Hwang JI, Jeon YH, Kim HY, Ahn JW, et al., 2012. Dissipation patterns of triazole fungicides estimated from kinetic models in apple. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 55(4):235-239.
[https://doi.org/10.3839/jabc.2012.037]

- Kwon HY, Lee HD, Kim JB, Jin YD, Moon BC, et al., 2009. Reduction of pesticide residues in field-sprayed leafy vegatables by washing and boiling. J. Food Hyg. Saf. 24(2):182-187.
- Lee JH, Park HW, Keum YS, Kwon CH, Lee YD, et al., 2008. Dissipation pattern of boscalid in cucumber under greenhouse condition. Korean J. Pestic. Sci. 12(1):67-73.
-
Lee MG, 2013. Management and regulation on the minor use of pesticides in Korea and foreign countries. Korean J.Pestic. Sci. 17(3):231-236.
[https://doi.org/10.7585/kjps.2013.17.3.231]

-
Lee MG, Kang GR, Kim TS, Yang YS, Kim SG, 2019. Monitoring and Risk Assessment of Pesticide Residues in Dried Pepper and Pepper Powder in Gwangju. Korean J. Pestic. Sci. 23(1):40-50.
[https://doi.org/10.7585/kjps.2018.23.1.40]

-
Leichter CA, Thompson N, Johnson BR Scott JG, 2013. The high potency of ME5343 to aphids is due to a unique mechanism of action. Pest Biochem Physiol. 107(2):169-176.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2013.06.009]

-
Li L, Sun X, Zhao X, Xiong Y, Gao B, et al., 2021. Absolute Configuration, Enantioselective Bioactivity, and Degradation of the Novel Chiral Triazole Fungicide Mefentrifluconazole. J. Agric. Food Chem. 69(17):4960-4967.
[https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07947]

- MDA, 2022. New active ingredient and new use special registration reviews. https://www.mda.state.mn.us/chemicals/pesticides/regs/newreviews, (Accessed Feb. 25. 2022).
- MFDS, 2022. Notification of the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Notification No. 2022-7. https;//www.law.go.kr, (Accessed Feb. 14. 2022).
- NAQS, 2021. National Agricultural Products Quality Management Service_Agricultural Product Residual Pesticide Analysis Results. https://www.data.go.kr/data/15047546/fileData.do, (Accessed Dec. 28. 2021).
-
Noh HH, Kwon HY, Kim DB, Kim CJ, Lee HS, et al., 2019. Application of QuEChERS sample preparation method for the residual analysis of newly registered pesticide pydiflumetofen in agricultural product. Korean J. Pestic. Sci. 23(2):86-95.
[https://doi.org/10.7585/kjps.2019.23.2.86]

- Park DS, Seong KY, Choi KI, Hur JH, 2005. Field tolerance of pesticides in the strawberry and comparison of biological half-lives estimated from kinetic models. Korean J. Pestic. Si. 9(3):231-236.
-
Park JS, Lee HS, Lee SJ, Shin HS, Shim JH, et al., 2020. Development and validation of simultaneous analytical method for the detection of mefentrifluconazole and triticonazole fungicide in agricultural crops. Korean J. Environ. Agric. 39(2):130-137.
[https://doi.org/10.5338/KJEA.2020.39.2.17]

- RDA, 2018. Agricultural technology guide_perilla p.10.
-
Ripley BD, Ritcey GM, Harris CR, Denomme MA, Lissemore LI, 2003. Comparative persistence of pesticides on selected cultivars of specialty vegetables J. Agric. Food Chem. 51(5):1328-1335.
[https://doi.org/10.1021/jf020139o]

-
Xie J, Zheng Y, Liu X, Dong F, Xu J, et al., 2019. Human health safety studies of a new insecticide: Dissipation kinetics and dietary risk assessment of afidopyropen and one of its metabolites in cucumber and nectarine. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology. 103:150-157.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2019.01.025]

Joo Un Park, Analysis Technology and Tomorrow, Researcher, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1968-5690
Byung Jin Bae, Analysis Technology and Tomorrow, Researcher
Sang Won Woo, Analysis Technology and Tomorrow, Researcher
Hye Jin Jeong, Analysis Technology and Tomorrow, Researcher
You Jin Jang, Analysis Technology and Tomorrow, Researcher
Jong Woo Park, Analysis Technology and Tomorrow, Researcher
Seok Chai, Analysis Technology and Tomorrow, Researcher, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3077-7358
Kun Sik Lee, Analysis Technology and Tomorrow, Researcher
Young Soo Keum, Department of Bioresources and Food Science, Konkuk University, Professor
Kee Sung Kyung, Department of Environmental and Biological Chemistry, College of Agriculture, Life and Environment Sciences, Chungbuk National University, Professor
Jang Eok Kim, School of Applied Biosciences, Kyungpook National University, Professor
Tae Hwa Kim, Analysis Technology and Tomorrow, Researcher, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2223-9891