포도(Vitis vinifera L.) 중 Pyrimethanil 및 Methoxyfenozide의 생산단계 잔류허용기준 설정
초록
본 연구는 포도에 대한 pyrimethanil과 methoxyfenozide의 잔류량 변화를 측정하여 약제별 잔류특성을 파악하고, 잔류량 감소추이를 산출함으로써 생산단계 잔류허용기준(Pre-Harvest Residue Limit, PHRL) 설정을 위한 기초자료로 활용하고자 수행하였다. Pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide 농약을 안전사용기준에 준하여 각각 포장 1, 포장 2 지역으로 나누어 기준량 처리하였으며, 약제처리 2시간 후를 0일차로 하여 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10일차에 시료를 채취하여 분석하였다. 두 약제 모두 HPLC/DAD를 이용하여 분석하였으며, 분석정량한계(Method Limit of Quantitation, MLOQ)는 0.01 mg kg−1이었다. 분석결과, 분석법의 회수율은 80.6~102.5%이었으며, 표준편차는 모두 10% 미만이었다. 포도 중 각 농약에 대한 생물학적 반감기는 pyrimethanil의 경우 7.7일(포장 1), 7.4일(포장 2)이었으며, methoxyfenozide의 경우 5.1일(포장 1), 6.1일(포장 2)이었다. 잔류회귀감소식을 이용한 pyrimethanil과 methoxyfenozide의 생산단계 잔류허용기준은 각각 수확 10일 전 8.90과 5.51 mg kg−1으로 제안하였다.
Abstract
The present study was aimed to predict the pre-harvest residue limits (PHRLs) of pyrimethanil (fungicide) and methoxyfenozide (insecticide) in grape, and to estimate their biological half-lives and residual characteristics. The pesticides were sprayed once on grape in two different fields 10 days before harvest. At the end of 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7 and 10 days after application, samples were harvested for further analysis. The residual pesticides were extracted with acetonitrile and partitioned with dichloromethane, and the highperformance liquid chromatography with diode array detector (HPLC/DAD) was employed for the residue analysis. The results obtained in the present study show that the limit of detection of both pesticides were found to be 0.01 mg kg−1. The recoveries of these pesticides were ranged between 80.6% and 102.5% with coefficient of variation lower than 10%. The biological half-lives of both pesticides were observed in field 1 and field 2 which shows 7.7 and 7.4 days for pyrimethanil and 5.1 and 6.1 days for methoxyfenozide, respectively. Further, the PHRL of pyrimethanil and methoxyfenozide was found to be 8.90 mg kg−1 and 5.51 mg kg−1, respectively at 10 days before harvest. Consequently, the present study suggests that the residual amounts of both pesticides will be lower than the maximum residue limits (MRLs) when grape is harvested.
Keywords:
Grape, Pre-Harvest Residue Limit, Maximum Residue Limit, Pyrimethanil, Methoxyfenozide키워드:
포도, 생산단계 잔류허용기준, 잔류허용기준서 론
농약은 병해충 및 잡초로부터 농산물을 보호하고 생산량 증대와 품질 향상에 기여하는 중요한 농자재이다. 살포된 농약은 수확시기까지 분해 및 소실되어 작물에 잔류하지 않는 것이 가장 이상적이지만 여러 형태의 화학구조를 가지고 있는 특성상 사용이 끝난 후에도 농작물이나 환경 중에 잔류되는 경우가 있다(Kim et al., 2009).
이에 국가에서는 농산물 중 농약잔류허용기준(Maximum Residue Limit, MRL)을 설정하여 잔류농약에 대한 관리를 하고 있다. 그러나 유통단계 중 시행되는 잔류농약검사는 잔류량이 최대잔류허용기준량을 초과할 경우 이미 유통되었을 가능성이 높아 농산물의 회수가 어려우며, 부적합 농산물은 용도전환 또는 폐기처분되어 농민들에게 경제적 손실을 발생시킨다. 이와 같은 문제를 방지하고, 생산단계 농산물의 안전관리를 위하여 국가에서는 생산단계 잔류허용기준(Pre-harvest Residue Limit, PHRL)을 설정하였다. 생산단계 잔류허용기준은 생산단계 농산물에 대한 안전성을 평가하는 기준으로 수확 전 일정 시점의 기간 동안 농약의 잔류량을 조사하고, 생물학적 반감기를 산출하여 수확 시 잔류량을 예측함으로써 MRL을 초과할 가능성이 있는 부적합 농산물의 유통을 사전에 차단하는 데 목적이 있다(농림수산식품부, 2009).
5대 과수 중 하나인 포도는 갈매나무목 포도과에 속하는 낙엽성 덩굴식물로 미네랄, 비타민, 철분 등의 영양분이 풍부하다고 알려져 있다. 또한 포도의 폴리페놀 성분이 심혈관질환, 암, 동맥경화 등의 질병 예방에 효과적이라는 연구결과가 보고되면서 포도의 생산량과 소비량이 점차 증가하고 있다(Kim et al., 2012). 그러나 포도에 대한 생산단계 잔류허용기준은 2014년 기준 42개 성분에 대해서만 설정되어 있어 적용 농약 품목의 확대가 필요한 실정이다(식품의약품안전처, 2014).
본 연구는 포도 생산단계 중 pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide의 잔류량을 분석하여 약제별 잔류 특성 및 반감기 산출을 통해 생산단계 잔류허용기준 설정에 기여하고자 수행하였다.
재료 및 방법
시험농약
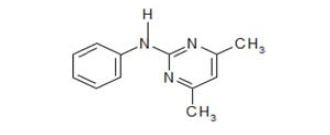
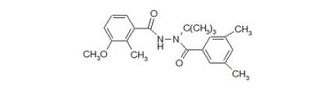
본 연구에 사용된 pyrimethanil (99.9%, Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH, Germany) 및 methoxyfenozide (99.6%, Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH, Germany)의 표준품은 원제사로부터 구입하여 사용하였고, 살포용 농약 pyrimethanil 37% 액상수화제(상표명: 미토스, 바이엘 크롭사이언스(주)) 및 methoxyfenozide 21% 유제(상표명: 런너, 동부팜한농(주))는 시중에서 구입하여 사용하였다. 두 약제의 화학구조식 및 이화학적 성질은 Table 1과 같다.
시약, 재료 및 기구
잔류농약의 분석을 위해 사용한 dichloromethane, acetonitrile, n-hexane, methanol 및 ethyl acetate는 GR급을 사용하였으며, sodium sulfate anhydrous 및 sodium chloride는 EP급을 사용하였다. 정제에 사용한 SPE Florisil 1 g cartridge는 Phenomenex (USA)사의 제품을 구입하였다. 또한 약제 살포 시 동력식 분무기를 사용하였으며, 잔류농약 분석 시 시료균질기(AM-10, Nissei, Nihonseiki Kaisha Ltd., Japan)와 진공회전증발농축기(EYELA NE-1001, Tokyo Rikakikai Co., Ltd., Japan)를 사용하였다. 포도 중 pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide의 잔류량은 DIONEX UltiMate 3000(Thermo scientific, USA)을 이용하여 분석하였다.
시험작물 및 시험포장
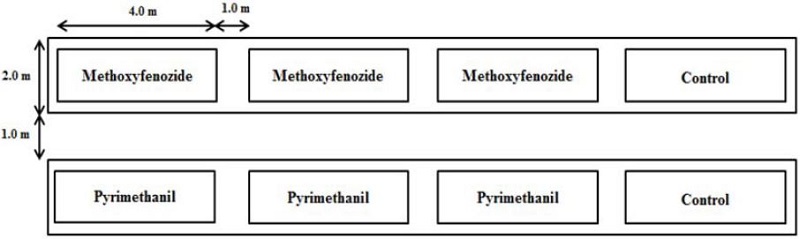
시험작물인 포도는 경기도 가평군 북면 소법리의 포도 재배지 2 포장을 임차하여 10일간(2013년 9월 10일~2013년 9월 20일) 시험을 진행하였다. 포장 1, 2의 시험 구획은 24m2으로 약제처리별 3반복 배치하였으며, 각각의 처리구 사이에 1 m의 완충구를 두고 시험을 수행하였다(Fig. 1).
약제처리 및 시료채취
포도에 대한 시험농약의 살포는 작물보호지침서(KCPA, 2012)의 안전사용기준에 준하여 희석한 후 동력식분무기를 사용하여 1회 살포하였고, 시험 농약 살포 2시간 후를 0일차로 하여 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10일차에 약 1.5~2 kg의 시료를 채취하였다. 채취한 시료는 밀봉한 후 즉시 분석 장소로 운반하였으며, 처리구별로 세절 및 혼합하여 -20°C 이하의 냉동고에서 보관 후 분석 시 사용하였다. 본 시험에서 포도에 살포한 약제의 안전사용기준 및 잔류허용기준(Maximum Residue Limits, MRL)은 Table 2에 제시하였다.
분석검출한계
Pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide의 분석검출한계는 최소검출량, 최종 부피, 시료주입량, 시료량 등을 고려하여 산출하며 아래의 식과 같이 산출하였다.
표준검량선 작성
시험농약의 표준물질인 pyrimethanil (99.6%) 100.4 mg 및 methoxyfenozide (99.6%) 100.4 mg을 100mL acetonitrile에 녹여 1,000 mg L−1 stock solution을 조제한 후 단계별로 희석하여 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 및 5.0 mg L−1의 working solution을 조제하였다. 그 후 각각 일정량을 HPLC에 주입하여 나타난 chromatogram상의 peak면적을 기준으로 검량선을 작성하였다.
포도 중 잔류농약 분석
포도 중 잔류된 pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide를 추출하기 위하여 세절한 시료 20 g에 acetonitrile 100 mL를 가하여 homogenizer로 10,000 rpm에서 3분간 마쇄·추출하였다. 추출액 중 acetonitrile을 감압여과 및 농축한 후 증류수 100 mL, 포화식염수 50 mL를 첨가하여 dichloromethane 80, 70 mL로 2회 분배하였으며, 감압농축 후 dichloromethane 5 mL로 재용해 하였다. Pyrimethanil의 정제는 SPE Florisil 1 g cartridge에 dichloromethane 5 mL로 pre-washing한 후 추출액 5 mL를 모두 loading하여 버린 후 전개용출용매(dichloromethane:methanol = 95:5, v/v) 5 mL로 용출시켰다. Methoxyfenozide의 경우 SPE Florisil 1 g cartridge에 dichloromethane 5 mL로 pre-washing한 후 추출액 5 mL를 모두 loading하고 전개용출용매 1 (n-hexane:dichloromethane = 50:50, v/v) 10 mL로 세정하였다. 이후 전개용출용매 2(dichloromethane:ethyl acetate = 80:20, v/v) 6 mL를 이용하여 용출시켰다. 두 약제 모두 용출액을 감압농축한 건고물을 acetonitrile 2 mL로 재용해하여 필터링여과(0.2 μm membrane filter) 한 후 HPLC/DAD에 10.0 μL 주입하여 최종 분석하였으며, 분석조건은 Table 3과 같다.
포도 중 회수율 분석
무처리 포도 시료 20 g을 각각 칭량하여 표준용액 1 mg kg−1 표준용액 2 mL, 10 mg kg−1 표준용액 1 mL를 가한 후, 분석검출한계의 10배(0.1 mg kg−1), 분석검출한계의 50배(0.5 mg kg−1) 수준이 되도록 균일하게 혼합하여 30분간 방치한 후 상기의 분석과정을 수행하여 회수율을 산출하였다.
시험농약의 생물학적 반감기 및 생산단계 농약잔류허용기준
포도의 생산단계 중 시험약제의 잔류량은 표준검량선을 사용하여 산출하였으며, 생물학적 반감기 및 생산단계 농약잔류허용기준(PHRL)은 식품의약품안전처에서 제공하는 잔류성 시험성적 회귀분석 검정표를 이용하여 산출하였다.
결과 및 고찰
시험기간 중 기상조건과 포도의 중량
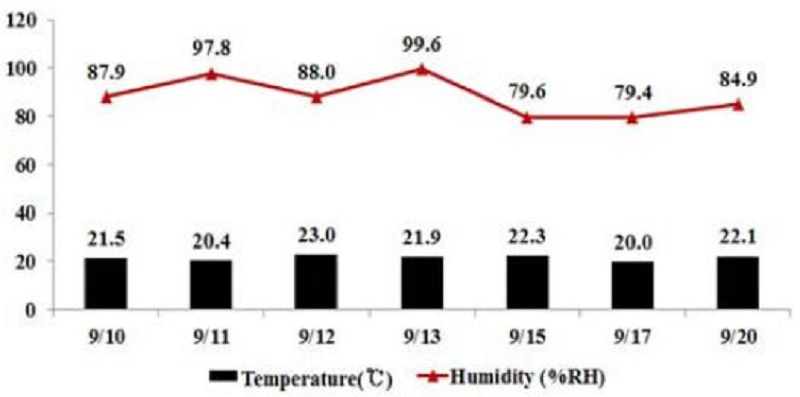
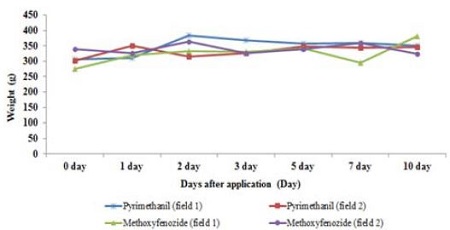
2013년 9월 10일부터 2013년 9월 20일까지의 시험기간 중 포장 1, 2 시설 내의 평균기온 범위는 20.0~23.0°C이었으며, 평균습도의 범위는 79.4~99.6%이었다(Fig. 2). 시험약제 살포 후 포장 1, 2에서 수확 한 포도의 평균무게는 274.3-383.2 g이었으며, 첫 번째 수확일 대비 마지막 수확일까지 대상작물의 평균증체율은 114.8% (Fig. 3)로 비대생장에 의한 잔류농약의 희석효과는 적을 것으로 판단된다.
표준검량선 작성
포도 중 잔류농약 분석을 위한 표준검량곡선을 작성한 결과, 두 약제 모두 상관계수(R2)가 0.99이상으로 높은 직선성을 확인하였다(Table 4).
분석검출한계 및 회수율
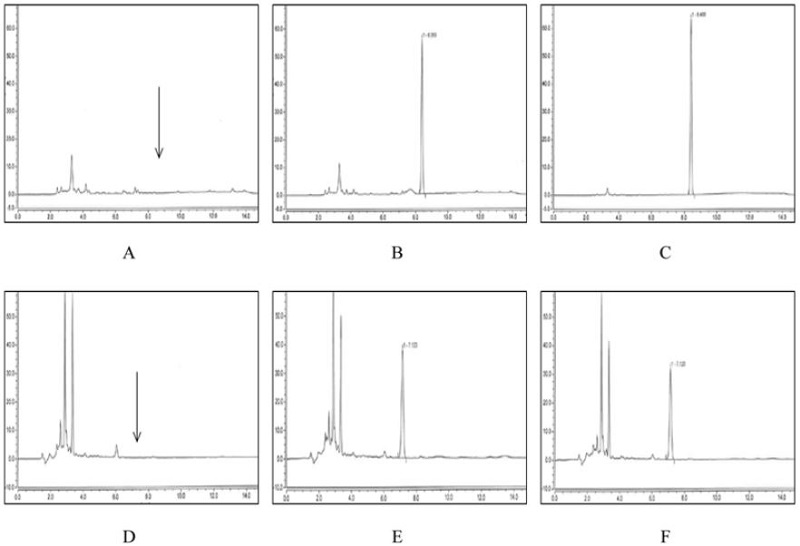
포도 중 pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide의 분석검출한 계는 모두 0.01 mg kg−1이었으며, pyrimethanil의 회수율은 85.5~88.8%, methoxyfenozide의 경우 80.6~102.5%로 두 약제 모두 식품의약품안전처의 단성분 분석 회수율 범위인 70~120%, 변이계수 10% 이내의 기준을 만족하여(Table 5) 잔류특성을 구명하기에 효율적인 분석방법이라 판단된다. 상기 분석방법에 의한 pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide의 머무름 시간은 각각 8.41분과 7.12분이었다. HPLC/DAD로 분석한 시험약제의 무처리, 회수율 및 처리구의 대표적 크로마토그램은 Fig. 4와 같다.
포도 생산단계 중 잔류량 변화에 따른 생물학적 반감기
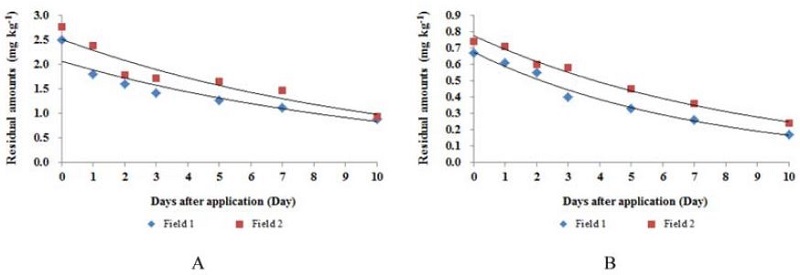
포도 생산단계 중 pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide를 안전사용기준에 준하여 포장 1, 포장 2에 각각 1회 기준량 살포하여 일자별 잔류량을 분석하였다. Pyrimethanil 기준량 처리 시 초기 농도는 포장 1에서의 초기 농도는 2.50 mg kg−1, 포장 2에서의 초기 농도는 2.77 mg kg−1이었고, methoxyfenozide의 경우 포장 1에서 0.67 mg kg−1, 포장 2에서 0.74 mg kg−1으로 시험포장간의 초기 잔류량은 큰 차이가 없었다(Fig. 5). 두 약제의 초기 잔류량 모두 MRL(pyrimethanil: 5.0 mg kg−1, methoxyfenozide: 2.0 mg kg−1, MFDS, 2014) 이하로 나타났다. 이는 Han 등 (2003)의 연구에서 같은 약제를 살포한 결과 표면이 울퉁불퉁한 딸기에서의 초기 잔류량이 포도보다 높은 것을 보면, 표면이 매끄럽고 과실이 뭉쳐져 있는 포도의 특성상 초기 잔류량이 낮게 나온 것이라 판단된다.
포도 중 pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide의 잔류량은 약제 살포 후 시간이 지남에 따라 감소하는 경향을 보였다. 잔류 농약의 감소 경향은 농약자체의 이화학적 특성, 제제형태, 대사 및 분해, 처리 후 수확일까지의 경과일수, 환경조건 등에 의한 영향을 받은 것으로 사료된다(Lo et al., 2004).
식품의약품안전처에서 제공한 시험농약의 잔류성 시험성적 회귀분석 검정표를 통해 각각 시험포장의 잔류량에 따른 잔류감소 회귀식을 산출한 결과, pyrimethanil의 경우 포장 1에서 y=2.0678e−0.0899x(R2=0.9112), 포장 2에서 y=2.5160e−0.0936x(R2=0.9138)이었으며, methoxyfenozide의 경우 포장 1에서 y=0.6717e-0.1364x(R2=0.9850), 포장 2에서 y=0.7746e−0.1130x(R2=0.9921)이었다(Fig. 5). 잔류감소 회귀식에 의해 산출된 두 농약의 생산단계 중 생물학적 반감기는 pyrimethanil의 경우 포장 1에서 7.7일, 포장 2에서 7.4일 이었으며, methoxyfenozide의 경우 각각 5.1, 6.1일로 나타났다. 포장간의 반감기 차이는 크지 않았으나 단감 중 pyrimethanil의 반감기는 15.6일(Lee et al., 2012), 배추 중 methoxyfenozide의 반감기는 3.5일(Lee et al., 2009)인 선행연구결과와 비교하였을 때 차이를 보였다. 이는 약제의 반감기가 농약 자체의 특성과 환경조건은 물론 대상작물의 종류에도 영향을 받기 때문이라 판단된다.
생산단계 잔류허용기준 설정
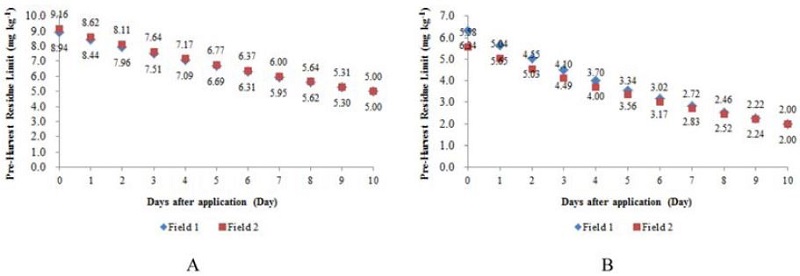
생산단계 잔류허용기준(PHRL)은 수확 전 일정 시점에 잔류 허용량을 설정하여 수확 시 농약의 잔류량이 MRL을 초과하지 않도록 설정한 기준으로 생산단계 포도의 일자별 잔류량을 이용하여 pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide의 생산단계 잔류허용기준을 산출하였다. 포도 중 pyrimethanil의 MRL은 5.0 mg kg−1이고, methoxyfenozide의 경우 2.0 mg kg−1으로 pyrimethanil의 수확 10일 전 생산단계 잔류허용기준은 포장 1에서 8.90, 포장 2에서 9.16 mg kg−1이었으며, methoxyfenozide의 수확 10일 전 생산단계 잔류허용기준은 포장 1에서 6.45 mg kg−1, 포장 2에서 5.51 mg kg−1로 나타났다. Pyrimethanil 및 methoxyfenozide의 수확 10일 전 잔류량이 각각 8.90 mg kg−1, 5.51 mg kg−1 이하로 나타나면 수확 시 잔류량이 MRL 이하로 잔류할 것으로 예측된다(Fig. 6). 본 연구결과는 부적합 농산물의 유통을 사전에 방지하여 소비자는 안전한 농산물을 섭취하고, 생산자는 불필요한 경제적 손실을 최소화 할 수 있는 농산물 안전관리에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
Acknowledgments
본 성과물은 식품의약품안전처에서 시행한 2013년 생산단계 농산물 중 농약의 잔류허용기준 설정 연구의 지원에 의해 이루어 졌으며, 이에 감사드립니다.
Literature cited
- Tomlin, C. D. S., (2009), The Pesticide Manual, British Crop Production Council, UK, p993-994.
- Tomlin, C. D. S., (2009), The Pesticide Manual, British Crop Production Council, UK, p764-765.
- Korea Crop Protection Association, (2012), 2012 Guideline of Pesticides Use, Korea Crop Protection Association.
-
Kim, J. H., S. K. Choi, Y. S. Yu, K. S. Yoon, and J. S. Seo, (2012), Physiologically Active Components and Antioxidant Capacity of Grapevine Leaves at Growth Stages, The Korean Journal of Food Science, 44(6), p772-778.
[https://doi.org/10.9721/KJFST.2012.44.6.772]

- Kim, S. W., E. M. Lee, Y. Lin, H. W. Park, H. R. Lee, M, J. Riu, Y. R. Na, J. E. Noh, Y. S. Keum, H. H. Song, and J. H. Kim, (2009), Establishment of pre-harvest residue limit(PHRL) of insecticide bifenthrin during cultivation of grape, The Korean Journal of Pesticide Science, 13(4), p241-248.
- Han, S. S., S. C. Lo, W. J. Kim, P. J. Park, and I. K. Kim, (2003), Residual Characteristics of Etofenprox and Methoxyfenozide in Chinese Cabbage, Analytical Science & Technology, 16(1), p70-71.
-
Lee, D. Y., Y. J. Kim, S. J. Lee, K. S. Cho, S. G. Kim, M. H. Park, and K. Y. Kang, (2012), Establishment of Pre-Harvest Residue Limit of Fungicides Pyrimethanil and Trifloxystrobin during Cultivation of Persimmon.
[https://doi.org/10.5338/KJEA.2012.31.1.45]

- Korean Journal of Environmental Agriculture, 31(1), p45-51.
- Lee, E. Y., H. H. Noh, Y. S. Park, K. Y. Kang, J. K. Kim, Y. D. Jin, S. S. Yun, C. W. Jin, S. K. Han, and K. S. Kyung, (2009), Residual Characteristics of Etofenprox and Methoxyfenozide in Chinese Cabbage, The Korean Journal of Pesticide Science, 13(1), p13-20.
- Lo, S. C., C. H. Hwang, M. S. Kim, S. Y. Ma, and S. S. Han, (2004), Residue analysis of insecicide thiodicarb in sweet persimmon and its safety evaluation, The Korean Journal of Pesticide Science, 8(3), p184-188.
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, (2014), Toxic substances residue standard such as pre-harvest agricultural products.