꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험법 개선안에 따른 농약 2종의 RT25 설정
 ; Juyeong Kim1
; Juyeong Kim1 ; Bo-Seon Kim1
; Bo-Seon Kim1 ; Ji-Yeong Choi1
; Ji-Yeong Choi1 ; Hyun Ho Noh2
; Hyun Ho Noh2 ; Chang-Young Yoon1
; Chang-Young Yoon1 ; Jin-A Oh3
; Jin-A Oh3
초록
꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험법은 시험작물에 농약을 살포하고 24시간 마다 잎을 채취하여 꿀벌에 노출시킨 후 꿀벌이 25% 이하로 치사하는 시간인 RT25 값을 측정하는 시험법이다. 이 시험법은 미국과 한국의 꿀벌 위해성평가단계에서 요구되며, RT25 값을 활용하여 작물에 대한 꿀벌 안전방사기간을 설정한다. 최근 미국의 PRTF (Pollinator Research Task Force)는 꿀벌 엽상잔류시험법의 한계를 인식하고 이를 개선하기 위해 링 테스트를 수행하였으며, 개선된 시험 방법을 공개하였다. 개선된 시험법은 알팔파 잎의 배치 방법, 꿀벌의 나이, 꿀벌 시험케이지, 농약 살포 방법 등을 구체적으로 명시하고 있다. 본 연구에서는 개선된 시험 방법에 따라 carbaryl WP와 dinotefuran WP의 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험을 수행하였다. 시험포장에서 재배한 알팔파가 40 cm 정도 높이로 자랐을 때 농약을 최대 살포량 기준으로 균일하게 살포하였다. 알팔파 잎은 농약살포 후 6 시간, 다음날부터 24 시간 간격으로 채취하였는데, 꿀벌 치사율이 25% 이하가 될 때까지 수행하였다. 시험결과 carbaryl WP는 국내 고시에 따라 시험한 RT25 값은 5일이었고 개선된 시험방법에서는 6일이었다. Dinotefuran WP의 경우 국내고시안과 개선안으로 시험한 결과 RT25 값이 모두 3일로 동일하였다. 향후 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험의 시험케이지와 꿀벌 채집방법을 국내 고시에 보다 세부적으로 반영할 필요가 있으며. 알팔파 잎의 잔류분석 결과를 시험결과에 반영하여 제시하는 것이 필요할 것으로 보인다.
Abstract
The foliar residual toxicity test method for bees involves applying pesticides to test crops and exposing bees to collected leaves every 24 hours to determine the RT25 value, the period during which bee mortality is 25% or less. This test method is required in the United States and Korea during the bee risk assessment stages, and the RT25 value is used to determine safe release periods for bees in relation to crops. Recently, the U.S. Pollinator Research Task Force (PRTF) recognized the limitations of the foliar residual test method for bees and conducted a ring-test to improve and publicize a revised test method. The improved method specifically addresses variables such as the placement method of alfalfa leaves, bee age, bee test cages, and pesticide application methods. In this study, the foliar residual toxicity tests were conducted on carbaryl and dinotefuran wettable powder (WP) according to the improved method. The pesticides were uniformly sprayed when the alfalfa grown in the test fields reached approximately 40 cm in height, and alfalfa leaves were collected 6 hours after spraying and then at 24-hour intervals until bee mortality fell below 25%. The test results showed that the carbaryl 50% WP had an RT25 value of 5 days according to domestic standards, and 6 days according to the improved method. For dinotefuran 10% WP, the RT25 value was 3 days in both the domestic and improved methods. It appears necessary to further detail the bee collection methods and test cages in domestic regulations. Additionally, incorporating the residue analysis results of alfalfa leaves may also be essential.
Keywords:
Carbaryl wettable powder, Dinotefuran wettable powder, Honeybee, RT25, The foliar residual toxicity test키워드:
꿀벌, 엽상잔류독성시험법서 론
꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험법은 알팔파 작물에 농약을 살포하고 24시간 마다 알팔파 잎을 채취하여 실험실에 가져와 꿀벌에 노출시켜 그 치사율과 영향을 평가하는 시험법이다. 미국은 EPA(Environmental Protection Agency) Test guidelines에 Honeybee toxicity of residues on foliage(OCSPP850.3030)가 등재되어 있으며 꿀벌 접촉독성 LD50값이 11 mg/bee 미만일 경우 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험 성적서를 제출하여야 하며, 또한 RT25 값이 8시간보다 크면 잔류독성이 있는 것으로 판단하여 농약라벨에 잔류독성을 표기하도록 규정하고 있다(USEPA, 2012, 2016). 우리나라에서는 2000년에 꿀벌 급성독성시험기준과 방법을 최초로 고시하였고, 2007년에 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험법을 추가로 고시하였다. 현재 우리나라에서는 1단계 꿀벌 위해성평가에서 위해성평가지수(HQ)가 50 이상일 경우 2단계 평가에서 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험성적서를 제출해야 한다. 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험에서 RT25가 1일 미만, 1일 이상 5일 미만, 5일 이상인 경우로 분류하여 각각 다른 주의사항 문구가 표시되고 5일 이상인 경우에는 적색 글씨로 “꿀벌에 독성 강함”으로 경고문구를 표시한다.
RT25 값은 농약을 최대살포량으로 살포하였을 때 꿀벌에게 독성을 미칠 수 있는 시간을 측정하는 것이다. 이 값은 화분매개벌을 사용하는 농가에서 농약을 사용할 때 화분매개벌의 안전방사기간 지침으로 활용할 수 있다.
국내에서는 2000년 이후 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험법과 관련한 연구가 지속적 수행되고 있다. Ahn et al., (2008)은 강낭콩 잎과 토마토 잎에 농약을 살포하고 실험실에서 꿀벌 및 뒤영벌을 노출시켜 안전방사기간을 제시하였다. 또한 Bae et al., (2013)는 침투이행성 농약을 토마토 모종에 처리한 후 토마토 잎을 채취하여 실험실에서 꿀벌을 노출시켜 시간별 꿀벌 치사개체수를 제시하였고, 침투이행성 농약의 경우 뿌리에서 잎으로 농약이 흡수 이행되며 꿀벌에 영향을 주는 것을 확인하였다. Cho et al., (2010)는 알팔파와 사과를 비가림 재배하여 시험농약을 최대농도로 살포한 후 잎을 채취하여 꿀벌에 노출시킨 후 RT25 값을 산정하였다. 이 연구에서는 수화제가 액제에 비해서 작물체 표면에 더 잔류하여 잔류독성을 더 오래 지속시키는 것을 밝혔다. Kim et al., (2009)는 딸기시설하우스에서 피프로닐 액상수화제를 살포한 후 딸기 잎을 실험실 내로 운반하여 잎을 잘게 잘라 15 g씩 원통형 철망케이지에 배치하여 꿀벌을 노출시켰으며 살포 후 28일까지도 90% 이상의 치사율을 보인 것을 확인하였다. 이와 같이 국내 연구는 꿀벌 엽상잔류시험법을 응용하여 알팔파 작물이 아닌 해당 농약을 살포하는 작물의 잎을 가지고 잔류독성을 평가하는 연구들이 주를 이루었다.
최근 EPA는 동일한 유효성분을 가진 농약이라도 RT25 값이 일정하지 않고 다를 수 있다는 사실을 인지하였다. 이에 따라 미국의 PRTF(Pollinator Research Task Force)에서 기존 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험의 시험방법을 개선하기 위한 ring test를 진행하고 보고서를 EPA에 제출한 바 있다(PRTF, 2022a; PRTF 2022b). PRTF에서는 학계, 정부기관, 산업계로 구성된 위원회를 구성하여 같은 농약을 가지고 시험을 진행하였다. 기존 시험법의 한계점은 시험케이지 규격, 시험케이지안의 알팔파 배치방법, 농약살포방법, 꿀벌 연령, 알팔파 재배 장소(비닐하우스 VS 야외재배), 환경요소(풍속, 기온, 습도) 등의 기준이 명확하지 않다는 것이다. 따라서 개선된 시험법에서는 시험케이지 규격을 구체화하고, 농약살포시 알팔파 높이는 20-40 cm, 알팔파 잎(12-15 cm)를 자르고 잎 전체를 대각선 배치, 3-5일령 일벌을 사용을 하는 등 세부항목을 명시하였다(PRTF, 2022b).
국내에서도 같은 농약품목에 대해 RT25 값이 다른 경우가 발생하고 있는 상황이므로 시험케이지와 시험작물의 크기, 배치방법 등에 대해 개선할 필요가 있다고 판단된다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 농약 2종(carbaryl WP, dinotefuran WP)을 선정하여 PRTF의 개선된 시험방법에 따라 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험을 진행하고 기존 국내 고시에 따라 시험한 시험성적서 RT25 값을 비교하여 개선된 시험법의 국내 적용가능성을 판단하고자 하였다.
재료 및 방법
꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험법 비교
Table 1은 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험의 국내 고시와 미국 EPA 시험법 개선안의 주요 내용을 비교한 표이다. 국내 고시의 시험용 용기는 스테인리스 철망(직경 15 cm×높이 5 cm) 원통형 덮개에 유리급식관을 끼우도록 되어있다. 개선안에서는 원통형 플라스틱 케이지(윗지름 11 cm, 밑지름 9 cm, 높이 14 cm)를 사용한다. 국내 고시에서는 알팔파 잎을 15 g을 채취하여 잘게 잘라서 케이지에 배치하지만 개선안에서는 알팔파 잎을 12-15 cm로 잘라서 잘게 자르지 않고 케이지에 대각선이나 수직으로 세워서 배치하면 된다. 꿀벌 나이의 경우는 국내 고시에는 1-7일령의 어린 일벌을 사용하도록 명시되어 있다. 개선안에서는 벌통의 번데기 소비판을 실험실에 가져와 항온항습 인큐베이터(34-35oC, 상대습도 45-90%)에서 꿀벌을 우화시켜 3-5일령의 일벌을 실험에 사용하도록 하고 있다. 또한 개선안에서는 알팔파 잎을 야외시험포장에서 실험실로 옮길 때 아이스박스(8-12oC)에 넣어 이동해야 한다. 국내 고시에서는 농약살포단계의 알팔파 작물의 크기, 잔류분석에 대한 내용이 명시되어 있지 않다. 개선안에서는 알팔파 작물의 높이가 20-40 cm일 때 농약을 살포한다. 농약살포 후 1시간 30분 후에 알팔파 잎을 채취하고 다음날 24시간마다 알팔파 잎을 채취하여 잔류농약 분석을 한다. 농약살포시 spray card를 배치하여 카드의 잔류농약 분석을 실시한다. 국내 고시에서는 약제살포 후 강우에 의한 영향을 피하기 위해 비가림 재배가 바람직하다고 되어있다. 개선안에서는 농약살포 후 최소 3시간 동안에는 비가 와서는 안되고 비가 올 경우 비가림을 캐노피 등을 이용하여 할 수 있다고 명시되어있다. 또한 비가 오지 않을 경우는 직사광선을 받는 등 자연스러운 풍화작용이 이루어지도록 비가림을 하지 않는 것을 원칙으로 한다.
시험생물
꿀벌(Apis mellifera)은 전라북도 국립농업과학원 양봉생태과 양봉장에서 건강한 봉군을 선발하여 사용하였다. 시험 시작 4주 전부터 시험봉군에 응애방제제 등의 약제 처리를 하지 않았다. 시험봉군에서 봉판과 먹이판을 가져와 온도 35oC, 상대습도 60% 조건으로 유지되는 항온 인큐베이터(DAIHAN Scientific Co., Korea)에 배치하였다. 인큐베이터 안에서 우화한 꿀벌을 별도의 케이지에 옮겨 우화일자를 기록하고 우화한지 3-5일된 일벌을 시험에 사용하였다.
시험작물
국립농업과학원에 설치된 시설망사하우스에서 알팔파 (Vernal품종)를 2021년 9월에 파종하여 재배하였다. 처리군 당 알팔파 면적은 20.48 m2 (1.6×12.8 m)이었다(Fig. 1). 알팔파 한 구역을 1.6 m×2 m 로 지정하였으며, 총 6개의 구역으로 나누었다. 처리군과 무처리군은 서로 다른 시설망사하우스에서 재배한 알팔파 구역을 지정하였다. 처리군과 무처리군 사이에 10 m 이상의 간격을 두었으며, 시험농약이 분산되지 않도록 가림막을 설치하여 시험농약 비산을 방지하였다.
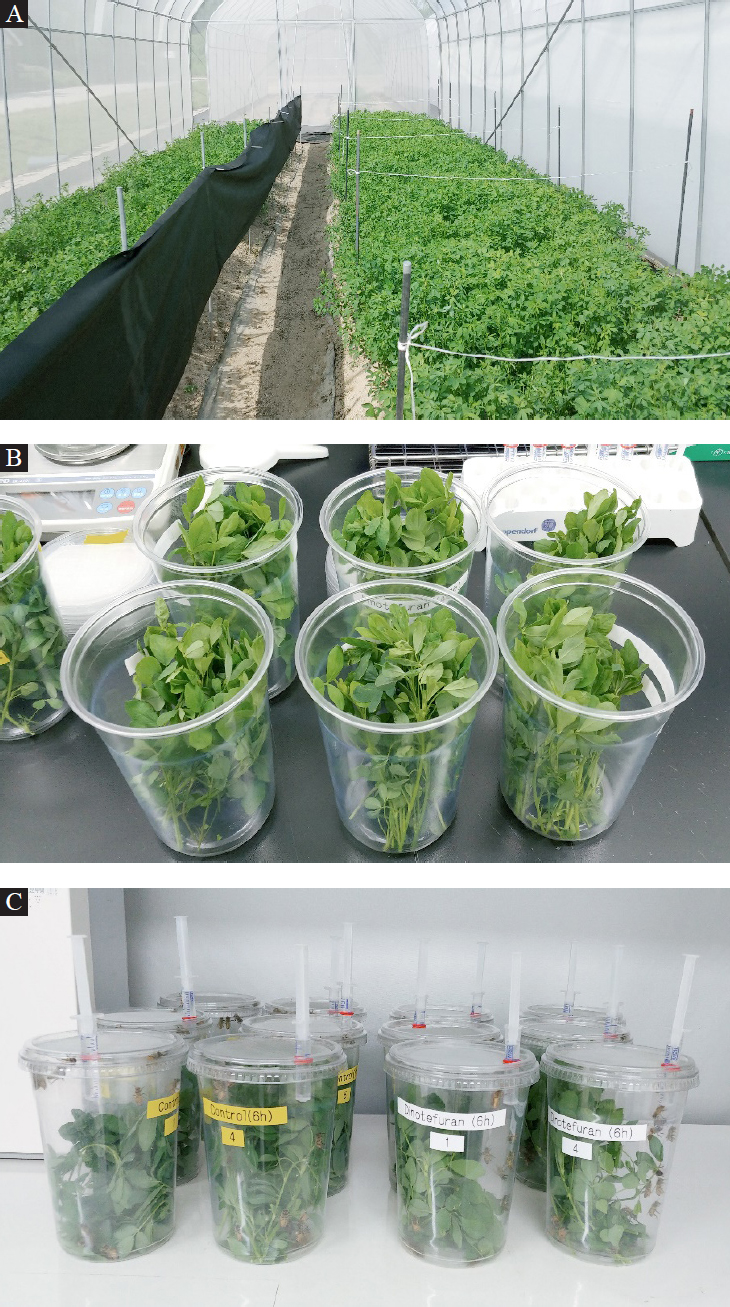

The test field plots and set-up for the foliar residual toxicity test: A, the alfalfa field plots; B, alfalfa foliage (15 cm length, 15 g weight) was placed vertically in each test cage; C, the overall experimental set-up.
알팔파 높이가 40 cm 정도 되었을 때 시험농약을 최대살포량 기준으로 살포하였다. 시험농약 처리 전 4주 동안 알팔파 재배지에 농약을 처리하지 않았다. 시설망사하우스는 지붕에 비닐개폐장치를 장착하여 비가 올 경우 지붕을 닫아 알팔파에 비가 직접 맞는 것을 방지하였다.
시험농약
시험 농약은 EPA 개선안으로 시험한 값과 기존의 데이터를 비교하기 위해 기존 RT25 값이 5일인 carbaryl 50% WP와 3일인 dinotefuran 10% WP를 사용하였다.
시험용기
시험용기는 투명플라스틱 재질의 원통형 케이지(윗지름 11 cm, 밑지름 9 cm, 높이 14 cm)와 망사가 부착된 덮개를 제작하여 사용하였다(Fig. 1). 덮개에 구멍을 뚫어 팁을 제거한 3 ㎖ 주사기를 꽂아 시험기간 동안 50% (w/w) 자당용액을 공급하였다. 먹이공급기와 알팔파 잎이 접촉되지 않도록 주의하였다.
꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험
본 시험 방법은 최근에 미국 EPA의 기존 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성 시험법(OCSPP 850.3030)을 개정한 ring-test 시험법을 적용하여 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성을 평가하였다. 각 처리군은 시험농약의 최대살포농도로 희석하여 압축식 분무기(MSB-100S, Maruyama, Japan)를 이용해 알팔파 잎에 골고루 살포하였다. 무처리군은 수돗물을 살포하였다. 살포작업은 바람과 강우가 없는 오전에 진행하여 강우에 의한 영향이 없도록 하였다. Carbaryl WP에 대한 엽상잔류독성시험은 2022년 5월에 진행하였으며, dinotefuran WP는 9월에 시험을 진행하였다. 시험약제 처리 후 알팔파 잎 채취시간은 6시간 이후 24시간 간격으로 하였으며, 알팔파 상단에서부터 15 cm 길이로 채취한 후 8-12oC를 유지하는 아이스박스에 보관하여 실험실로 운반하였다. 실험실에서 채취한 잎을 15 g씩 시험용 케이지에 수직으로 담아 준비하였다. 시험 시작 전 CO2 가스로 꿀벌을 마취시킨 후 준비된 시험케이지에 25마리씩 6반복으로 노출시켰다. 시험기간 동안 실험실 환경은 온도 25±2oC, 상대습도 60±10%, 암실 조건을 유지하였다.
치사개체 및 이상증상 확인
약제 노출 후 6시간, 24시간의 치사개체 및 이상증상을 관찰하였다. 처리군의 치사율이 무처리군에 비해 25% 미만으로 치사할 때까지 24시간 간격으로 알팔파 잎을 채취하여 노출시켰으며, 그 시점의 잎 채취시간(일)을 RT25(Residual time to 25% mortality)로 정하고 시험을 종료하였다. 약제 노출 후 정상적인 개체와 치사한 개체(dead bees, D), 이상증상을 보이는 개체(abnormal bees, A)를 관찰하여 기록하였으며, 치사한 개체는 시험종료 시까지 제거하지 않고 시험케이지 내에 방치하였다. 약제 노출 후 이상증상으로는 무기력한 상태, 걷지 못하고 보행장애를 가진 상태, 과다행동을 보이는 상태 등이 관찰되었다.
잔류분석
농약살포 직전에 한 구역 당 cellulose 재질의 spray card (78.5 cm2) 1개씩을 알팔파 잎 위에 배치하였다. 농약살포 후 spray card를 수거하여 분석전까지 -20oC에 보관한 후 한국농업기술진흥원에 의뢰하여 잔류농약을 분석하였다. 잔류농약분석은 농약살포 후 1시간 30분 뒤에 알팔파 잎을 50 g씩 채취하였고, 약제처리 후 경과시간에 따라 잎을 채취하여 엽상잔류량을 분석하였다.
알팔파 잔류농약 분석법
드라이아이스를 첨가하여 믹서기로 균질화한 알팔파 시료를 10 g을 tall beaker에 칭량하고 80% acetonitrile 100 mL를 첨가한 후 homogenizer를 이용하여 12,000 rpm으로 3분간 추출하였다. 추출액은 Celite 545를 이용하여 감압 여과하였으며, acetonitrile 20 mL로 용기 및 잔사를 씻어 앞의 여과액과 합하였다. 이 여과액을 40oC 수욕상에서 감압 농축하여 유기용매를 제거하고 증류수 150 mL와 포화 NaCl 50 mL이 들어있는 분액여두로 옮긴 후 dichloromethane 50 mL를 가하여 250 rpm에서 10분간 진탕하는 방식으로 2회 분배하였다. 분배 후 유기용매 층을 anhydrous sodium sulfate에 통과시켜 탈수하고 이를 40oC 수욕상에서 감압 농축하여 건고한 후 acetonitrile 10 mL로 재용해하여 정용하였다. 이 중 2 mL를 취하여 PSA(Primary Secondary Amine) 25 mg과 MgSO4 150 mg이 들어있는 d-SPE tube에 가한 후 vortex mixer로 약 30초간 교반하는 방법으로 정제하였다. 정제한 시료는 12,000 rpm에서 원심분리 한 후 0.2 μm syringe filter로 여과한 시료를 Table 2에 제시한 방법을 이용하여 기기분석하였다.
Spray card 잔류농약 분석법
Conical tube에 spray card를 넣고 acetonitrile 20 mL 첨가하여 690 rpm에서 30분간 진탕 추출한 후 4,200 rpm에서 원심 분리하였다. 추출액은 0.2 μm syringe filter로 여과한 후 LC-MS/MS에 3 μL 주입하여 나타난 크로마토그램상의 피크면적을 이용하여 잔류농약을 분석하였다.
Spray card의 경우 20 mL의 acetonitrile을 이용하여 690 rpm에서 20분간 진탕 추출한 후 0.2 μm syringe filter로 여과하고 acetonitrile로 2배 희석하는 방법으로 matrix matching하여 Table 2에 제시한 방법으로 기기 분석하였다.
결과 및 고찰
기상조건
Carbaryl WP를 대상으로 꿀벌엽상잔류독성시험을 수행한 기간 동안 알팔파 포장의 기온은 평균 20.3oC, 습도는 62.7%이었다(Table 3). 비는 5월 26일, 30일에 각각 3 mm, 2.5 mm 내렸지만 비가 오기 전에 시설망사하우스의 지붕을 개폐기로 닫아서 작물에 비가 노출되지 않도록 하였다. 실험실내 관찰기간 중 평균 온습도는 각각 26.0(±0.3)oC, 58.8(±0.4)%으로 시험기준에 적합하였다(Table 4; USEPA, 2012).
Dinotefuran WP를 살포한 후 알팔파 포장의 경우 기온이 평균 20.9oC, 습도는 63.9%이었으며, 시험기간 동안 비는 내리지 않았다(Table 3). 실험실 내 관찰기간 중 평균 온습도는 각각 24.8(±1.1)oC, 63.4(±7.9)%으로 시험기준에 부합하였다(Table 4; USEPA, 2012).
꿀벌 엽상잔류독성
Table 5와 Table 6은 각각 carbaryl WP 및 dinotefuran WP를 살포 후 6시간, 1일-6일까지 알팔파 잎을 채취하여 꿀벌에 노출하였을 때 24시간 후 꿀벌 치사 및 이상증상 개체수를 나타낸다. 모든 무처리군은 시험기간 동안 12.0% 이하의 치사율을 보였다. Carbaryl WP 처리군에서는 살포 후 6시간, 1일, 2일, 3일까지는 100%에 가까운 치사율을 나타냈고, 4일 후에는 84.7%, 5일 후에는 60.7%의 치사율을 나타냈다. 이후 6일 후에는 꿀벌 치사율이 16.7%로 감소하여 시험을 종료하였다. 그 결과, carbaryl WP의 RT25 값이 6일로 산정되었다(Table 7).

The number of worker bees that died or showed abnormal symptoms in the control and carbaryl 50% WP treated groups during the experimental period

The number of worker bees that died or showed abnormal symptoms in the control and dinotefuran 10% WP treated groups during the experimental period
Dinotefuran WP 처리군에서 살포 후 6시간 후에는 꿀벌 치사율이 100%이었으며, 1일 후에는 96.0%, 2일 후에는 68.7%이었고, 3일후에는 16.7%로 감소하여 시험을 종료하였다. 그 결과, dinotefuran WP의 RT25 값은 3일로 산정되었다(Table 7). 선행연구에서 dinotefuran 10% WP는 딸기잎에 대한 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험 결과, 딸기잎에 살포 후 17일까지 80% 이상의 높은 치사율이 나타났으나 제형이 다른 dinotefuran 20% WG는 처리 후 7일부터 잔류독성이 낮아지기 시작하여 14일 후에는 치사개체가 10% 미만이었다(Ahn et al., 2013). 또한 미국 EPA의 농약별 RT25 값을 보면 carbaryl 80% WP를 흰꽃토끼풀(white clover)에 0.28-2.24 kg/ha 로 살포하였을 경우 RT25 값은 42 h보다 컸다(USEPA, 2024). Dinotefuran 20% SG를 알팔파에 0.15 kg/ha 로 살포하였을 때 RT25 값은 39 h이었다(USEPA, 2024). 즉, 농약의 제형 및 구조적 특성, 기상조건, 살포시기에 따라 동일한 약제더라도 농약의 잔류독성에 차이가 나타날 수 있다
엽상잔류량 분석
Table 8 및 Table 9는 각각 carbaryl WP 및 dinotefuran WP 살포 후 알팔파 잎을 채취하여 잔류분석한 결과를 나타낸다. 두 농약 모두 시간 경과에 따라 잔류량이 경시적으로 감소하였다. Carbaryl WP의 경우 살포 당일날은 102.24(±2.1) mg/kg 이였으며 24시간마다 잔류량이 감소하여 6일차에 16.99 mg/kg으로 감소하였다. 본 시험에서 carbaryl WP가 알팔파 잎에 40 mg/kg 이상이 잔류되었을 때 꿀벌 치사율 100%를 나타내었으며, 잔류량이 약 17 mg/kg가 되었을 때 치사율이 16.7%로 감소하였다. Kim et al., (2014)은 carbaryl WP의 꿀벌 엽상잔류독성시험을 수행하였으며, carbaryl WP를 추천농도(625 mg/kg)로 1.12 kg/ha을 메밀잎에 처리하였을 때, 살포 후 1일에는 메밀잎에서 180 mg/kg, 10일에는 110 mg/kg, 18일에는 18.6 mg/kg 이었다. 꿀벌 치사율은 약제 살포 후 21일까지 70% 이상으로 메밀잎에서 carbaryl이 장기간 잔류독성이 나타남을 보고하였다. 또한 인위적으로 강우조건을 모사하여 carbaryl 처리후 3일과 10일에 단위면적당 10 mm/day 물을 뿌렸을 때 처리후 11일에 메밀잎 엽상잔류량은 12.6 mg/kg으로 조사되었으며, 꿀벌 치사율은 2.7%로 감소하였다.

Residue amount of carbaryl in alfalfa leaf samples during the residual toxicity test of carbaryl 50% WP

Residue amount of dinotefuran in alfalfa leaf samples during the residual toxicity test of dinotefuran 10% WP
Dinotefuran WP의 경우 엽상잔류량은 살포 당일날은 8.19 mg/kg 에서 3일차에 2.85 mg/kg으로 감소하였다. Carbaryl WP 처리군에 비해 잔류량이 낮게 검출되었지만, 잔류량이 약 6 mg/kg이었을때 96%의 높은 꿀벌 치사율을 나타냈다.
Table 10 및 Table 11은 각각 carbaryl WP 및 dinotefuran WP 살포 후 채취한 spray card의 cm2 당 잔류량을 나타낸다. Spray card에 검출된 carbaryl WP 및 dinotefuran WP의 잔류량 범위는 각각 3.34-6.84 μg/cm2 및 0.235-0.884 μg/cm2 이었다. Spray card의 잔류분석 결과에서도 dinotefuran WP에 비해 carbaryl WP가 상대적으로 높은 잔류량을 나타내었다.

Residue amount of carbaryl in spray cards during the foliar residual toxicity test of carbaryl 50% WP

Residue amount of dinotefuran in spray cards during the foliar residual toxicity test of dinotefuran 10% WP
본 시험에서는 최근 PRTF에서 제안한 개선된 시험법에 따라 carbaryl WP, dinotefuran WP 농약 2종에 대한 꿀벌의 엽상잔류독성을 평가하였다. 국내 고시에 따라 시험한 carbaryl WP의 RT25 값은 5일이었고 개선된 시험방법의 RT25 값은 6일이었다. Dinotefuran WP의 경우 국내고시안과 개선안으로 시험한 RT25 값이 3일로 동일하였다. 기존 국내고시안과 새로 제안된 개선안의 시험결과를 비교한 결과 RT25 값이 크게 다르지 않았다. 국내 고시안에서는 시험케이지가 스테인리스 원형 철망으로 명시되어 있고 잎을 잘게 자르도록 되어있다. 하지만 개선된 시험법에서는 원통형 케이지에 잎을 12-15 cm 길이로 잘라 세워서 배치한다. 이 방식은 시험케이지 제작을 간편하게 하고 시험시간 및 절차를 간소화할 수 있으므로, 향후 고시안에 반영하는 것을 고려할 필요가 있다. 또한 기존 시험법은 1-7일령의 꿀벌을 사용해야한다고 명시하고 있으나, 꿀벌 수집방법에 대한 명확한 지침이 부족하다. 새로 제안된 시험법에서는 실험실에서 꿀벌을 우화시켜 3-5일령의 정확한 나이를 확인하고 시험에 사용할 수 있다. 따라서 꿀벌 나이 및 채집방법 또한 고시에 반영할 필요가 있으며, 향후 농약살포량 및 잔류량 확인을 위해 알팔파 잎의 잔류분석 결과를 시험결과에 반영하는 것도 고려해야 한다.
Acknowledgments
본 연구는 국립농업과학원 기관고유 연구사업(과제번호: PJ01579701)에 의해 수행되었습니다. 이에 감사드립니다.
이해상충관계
저자는 이해상충관계가 없음을 선언합니다
References
- Ahn KS, Oh MG, Ahn HG, Yoon CM, Kim GH, 2008. Evaluation of toxicity of pesticides against honeybee (Apis mellitera) and bumblebee (Bombus terrestris). Korean J. Pestic. Sci. 12(4):382-390. (In Korean)
-
Ahn KS, Yoon CM, Kim KH, Nam SY, Oh MG, Kim GH, 2013. Evaluation of acute and residual toxicity of insecticides registered on strawberry against honeybee (Apis mellifera). Korean J. Pestic. Sci. 17(3):185-192. (In Korean)
[https://doi.org/10.7585/kjps.2013.17.3.185]

-
Bae CH, Cho KW, Kim YS, Park HJ, Shin KS, et al., 2013. Honeybee toxicity by residues on tomato foliage of systemic insecticides applied to the soil. Korean. J. Pesti. Sci. 17(3):178-184. (In Korean)
[https://doi.org/10.7585/kjps.2013.17.3.178]

- Cho KW, Park HJ, Bae CH, Kim YS, Shin DC, et al., 2010. Residual toxicity of bifenthrin and imidacloprid to honeybee by foliage treatment. Korean J. Pestic. Sci. 14(3):226-234. (In Korean)
- Kim BS, Yang YJ, Park YK, Joeng MH, You AS, et al., 2009. Risk assessment of fipronil on honeybee (Apis mellitera). Korean J. Pestic. Sci., 13(1):39-44. (In Korean)
-
Kim DW, Yun WK, Jung CE, 2014. Residual toxicity of carbaryl and lime sulfur on the European honey bee, Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae) and buff-tailed bumble bee, Bombus terrestris (Hymenoptera: Apidae). J. Apic. 29(4):341-348. (In Korean)
[https://doi.org/10.17519/apiculture.2014.11.29.4.341]

- Pollinator Research Task Force, 2022a. Results of the Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Toxicity of Residues on Foliage (RT25) Ring Study: Phase II. California. USA
- Pollinator Research Task Force, 2022b. Honey bee Toxicity of Residues on Foliage (RT25) Study Pollinator Research Task Force – Summary of Results and Recommendations. California. USA
- USEPA, 2012. Ecological effects test guidelines: OCSPP 850.3030: honey bee toxicity of residues on foliage. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention.
- USEPA, 2016. Guidance on exposure and effects testing for assessing risks to bees; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA.
- USEPA, 2024. Residual Time to 25% Bee Mortality (RT25) Data. https://www.epa.gov/pollinator-protection/residual-time-25-bee-mortality-rt25-data, , (Accessed Apr. 11. 2024).
Kyongmi Chon, Department of Agro-food Safety and Crop Protection, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Rural Development Administration, Doctor of Philosophy, Conceptualization; Methodology; Investigation; Data Curation; Writing-Original Draft preparation; Writing-Review & Editing; Funding Acquisition; Project Administration, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2143-2614
Juyeong Kim, Department of Agro-food Safety and Crop Protection, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Rural Development Administration, Master, Methodolgy; Writing-Original Draft preparation; Investigation, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6413-1822
Bo-Seon Kim, Department of Agro-food Safety and Crop Protection, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Rural Development Administration, Research assistant, Investigation, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6053-6366
Ji-Yeong Choi, Department of Agro-food Safety and Crop Protection, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Rural Development Administration, Master, Investigation, https://orcid.org/0009-0006-0612-3660
Hyun Ho Noh, Residual Agrochemical Assessment Division, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Rural Development Administration, Doctor of Philosophy, Methodology; Writing-Review & Editing, http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7568-8490
Chang-Young Yoon, Department of Agro-food Safety and Crop Protection, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Rural Development Administration, Master, Investigation, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7220-5425
Jin-A Oh, Research policy planning division, Research Policy Bureau, Rural Development Administration, Doctor of Philosophy, Supervision, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1166-4377