구기자에서 5종 살비제에 대한 구기자혹응애의 감수성 평가
 ; Deog-Gee Park2 ; In-Su Hwang1 ; Kyung-Joo Lee1 ; Seong-Won Yoon1 ; Gun-Woo Lee1 ; Seungwan Son3 ; Jeong-Ill Joo1
; Deog-Gee Park2 ; In-Su Hwang1 ; Kyung-Joo Lee1 ; Seong-Won Yoon1 ; Gun-Woo Lee1 ; Seungwan Son3 ; Jeong-Ill Joo1
초록
구기자는 비타민이 풍부하여 노화억제, 면역증진 등에 도움을 주는 약용작물이다. 구기자의 생산량 감소에 영향을 주는 주요 해충 조사 결과, 47종 이었으며, 구기자혹응애(Eriophyes sp.) 는 잎의 기형을 유도하고 혹을 형성하여 생산량에 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다. 구기자혹응애의 방제체계를 세우기 위해 5종 살비제(cyflumetofen SC, acequinocyl SC, azocyclotin WP, etoxazole SC, flufenoxuron DC)의 약효를 발생후 약제처리와 발생전 약제처리로 구별하여 평가하였다. 시험 대상 살비제 중에 azocyclotin은 발생후 및 발생전 약제처리에서 모두 90% 이상의 약효를 보였다. cyflumetofen은 발생전 약제처리에서 높은 살비효과를 보였다. 시험약제 기준량과 배량 처리 3, 5, 7일 후 재래종 구기자에서 약해는 없었다. 따라서, 구기자혹응애의 효과적인 방제 방법으로 cyflumetofen SC와 azocyclotin WP를 이용하여 신초 발생 전 1주 간격으로 2회 살포가 적합할 것으로 판단된다.
Abstract
Gojiberry is important medicinal crop to show high efficacy in nerve pain and etc. In the pest occurrence survey, 47 species (6 orders, 24 families) was observed and gall mite was considered as major pests by inducing leaf curling and gall formation. The five acaricides (cyflumetofen, acequinocyl, azocyclotin, etoxazole and flufenoxuron) were evaluated to establish the proper management strategy by spraying differently as post- and pre-treatment of mite occurrence. The azocyclotin WP showed more than 90% of acaricidal efficacy in both treatments. The cyflumetofen SC was revealed high efficacy only in the pre-treatment of mite occurrence. There was no phytotoxicity at the recommended dose and even at the double dose for any of the test acaricides. The selected acaricides (azozyclotin and cyflumetofen) would be applicable to control gall mite in gojiberry (Eriophyes sp.) by spraying twice at an interval of one week before new shoots occur.
Keywords:
Gojiberry, Eriophyes sp. acaricides, Susceptibility키워드:
구기자, 구기자혹응애, 살비제, 감수성서 론
구기자혹응애는 구기자 나무(Lycium chinens Mill)에 기생하여 잎에 혹(mite gall)을 형성한다. 구기자 나무의 어린잎의 뒷면 표피세포에 침입하여 이상비대를 일으켜 혹을 형성하며 혹이 성장함에 따라 책상조직과 해면상조직의 세포도 이상비대를 하게 된다(Kim et al., 1971). 구기자의 잎, 꽃받침, 과병 등에 혹응애가 발생하면 조기낙엽, 미숙낙과의 원인이 되고 수확 후에는 열매를 흑변시켜 품질을 저하시킨다(Kim, 1965; Kim, 1968).
구기자혹응애(Eriophyd mite)는 기주특이성이 강하며 동일한 기주식물이라 할지라도 품종에 따라 기생률이 크게 다른 특징을 가진다(Ehara and Shinkaji, 1996). 구기자에 기생하는 혹응애로 국내에 보고된 종은 총 3종이다(Lee, 2006). Kim (1965)와 Kim et al. (1971)에 의해 Eriophyes kuko Kishida 로 처음 “구기자혹응애”라는 이름이 사용되었으며, 그 후 Kim (1989) 이 Aceria macrodonis (Keifer)를 미기록종으로 보고하면서 역시 “구기자혹응애”라는 이름을 사용하였고 원색약용도감(1994)와 한국수목해충목록집(1995)에 종명은 동일하고 속명이 각각 다른 Eriophyes와 Aceria로 개칭되어 있으나 동일종임이 확인되었다(Lee, 2006). Lee (2006)은 1996년 채집한 구기자에 기생하는 혹응애를 조사한 결과 Aceria tjyingi Keifer임을 밝혀 위의 2종을 포함하여 3종이 국내에 존재함을 기록하였다.
구기자혹응애는 가지 등에서 성충으로 월동한 후 이듬해 봄인 5월 초순부터 10월까지 연 6-7회 발생하며(Kim, 1968), 심한 경우에 그 피해율은 95~100%에 달한다고 하였다(Lee et al., 1994). Park et al. (1993)은 구기자혹응애의 월동처로 지제부, 순, 과육, 피해낙엽 등에서 월동하는 것을 확인하였고 재래종에 비하여 유성 2호, 중국 1호가 저항성이 강함을 확인하여 품종에 따른 저항성 차이가 있음을 밝혔다.
구기자의 새로운 품종은 구기자혹응애에 대부분 강한 내성을 보이나 약리 효과와 기능성이 우수한 신품종 개발에 구기자혹응애는 항상 걸림돌로 작용하고 있으며 신품종이 나온다 해도 몇 년이 지나면 구기자혹응애의 적응으로 인해 피해가 나타난다는 재배 농가의 경험담을 쉽게 들을 수 있다. 따라서, 구기자에서의 혹응애 관리를 효과적으로 하기 위해서는 다양한 농약의 등록이 필수적이며 이는 농가의 피해를 최소화할 수 있다. 게다가 정부주도의 PLS (positive list system)가 전작물에 전면 시행되면서 농민들의 농약잔류 불안감은 고조되고 있다. 더욱이 국내에는 아직 구기자 전용으로 등록된 살충제가 2종 뿐이어서 농약의 잦은 사용에 따른 해충의 저항성 발달로 농가피해가 우려되는 상황이다. 따라서 본 연구는 PLS에 적극적으로 대응하고 구기자 주요 해충인 구기자혹응애를 효율적으로 방제할 수 있는 전략수립을 위해 5종의 살비제에 대한 살포방법에 따른 약제 감수성과 약해를 검정하여 구기자에 전용 약제를 등록하기 위한 기초자료로 제공하고자 수행하였다.
재료 및 방법
해충목록
구기자에 발생하는 주요해충에 대한 조사는 화학약제 포장시험 효과검정을 수행한 2020년부터 2022년 7월까지 충남농업기술원 내의 구기자 재배포장과 기술원 산하 구기자 연구소 그리고 일부 충남과 대전 주변에 식재된 구기자에 발생하는 해충들을 조사하였다. 조사 때 마다 자주 관찰되는 수준에 따라 소(+), 중(++), 다(+++), 심(++++) 4단계로 구분하고 이를 Table 1에 기록하였다.
시험포장
살비활성 검정을 위하여 충남 예산에 위치한 충남농업기술원 내의 구기자 포장과 충남 청양에 위치한 구기자연구소 내의 구기자 포장을 선정하였다. 두 지역 모두 재래종의 구기자를 유지하고 있었고 구기자혹응애의 발생이 심각한 수준이었다. 구기자의 재식거리로 예산과 청양 모두 이랑 간의 간격은 150 cm였고 주 간의 간격은 50 cm였으며 수종의 나이는 예산의 경우 2년생, 청양의 경우 3년생이었다. 예산은 노지재배 형태였으며 청양은 비가림 재배형태였다.
시험약제 및 살포 방법
구기자혹응애의 약제감수성 시험에 사용한 약제는 총 5종이었다(Table 2). 이 약제들은 구기자에 미등록된 약제들로서 대부분 타 작물에 살비제 및 나방류 해충 방제용 약제로 사용되고 있다. 모든 약제는 추천되는 희석 농도로 자동 충전식 분무기인 ㈜한일에스퍼의 HP2010®을 사용하여 살포하였고 살포전 사전 혹수를 조사하였다. 시험약제를 살포한 후 비는 내리지 않았으며 약제에 영향을 줄 만큼 기상상황에 특이점은 없었다.
방제효과 평가
방제효과 시험은 2가지 방법으로 나누어 조사하였다. 1) 2020년에는 발생초기에 약제를 살포하는 방법으로 무처리구의 발생량이 100개 이상의 혹을 형성 하였을 때 1주 간격으로 2회 약제를 살포하고 최종 약제 처리 15일 후 혹 형성수를 조사하여 혹 형성율로 표기하였으며 무처리구 대비 방제효과를 조사하였다. 2) 2021년에는 발생전 약제를 살포하는 방법으로 구기자의 신초가 발생하기 전에 1주 간격으로 2회 약제를 살포하고 신초가 발생한 시점으로부터 약 30일 후 혹 형성수를 조사하여 무처리구 대비 방제효과를 조사하였다. 신초가 발생한 시점부터 약 30일 후에 혹형성수를 조사한 이유는 초기발생시 약제를 살포하고 효과를 검정하는 시점과 동일한 시기에 효과를 비교하기 위함이다.
5종의 살비제에 대하여 시험포장내 처리수는 무처리를 포함하여 6처리수를 두고 반복은 3반복 실시하였으며 반복당 주수는 기본 5주를 선정하고 혹의 형성 수에 따라 탄력적으로 조사주를 선정하였다. 혹응애는 밀도조사를 통하여 방제효과를 조사하기에 너무 작은 곤충이며 게다가 혹을 형성하여 내부 기생하면 관찰이 불가능하므로 무처리 대비 혹 형성율을 조사하여 방제가를 도출하였다. 약해유무는 3, 5, 7일 후 실시하였고 신초에서의 오글거림, 신초발생수, 반점수, 잎 주변의 갈변수를 조사하였다. 방제가 도출식은 다음과 같다.
통계분석
약제별 실내 살충활성과 포장 방제효과 비교는 SAS 통계프로그램(SAS Institute, 2011)을 이용하여 Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (DMRT)로 평균간 유의성 차이를 검정하였다.
결과 및 고찰
구기자 해충
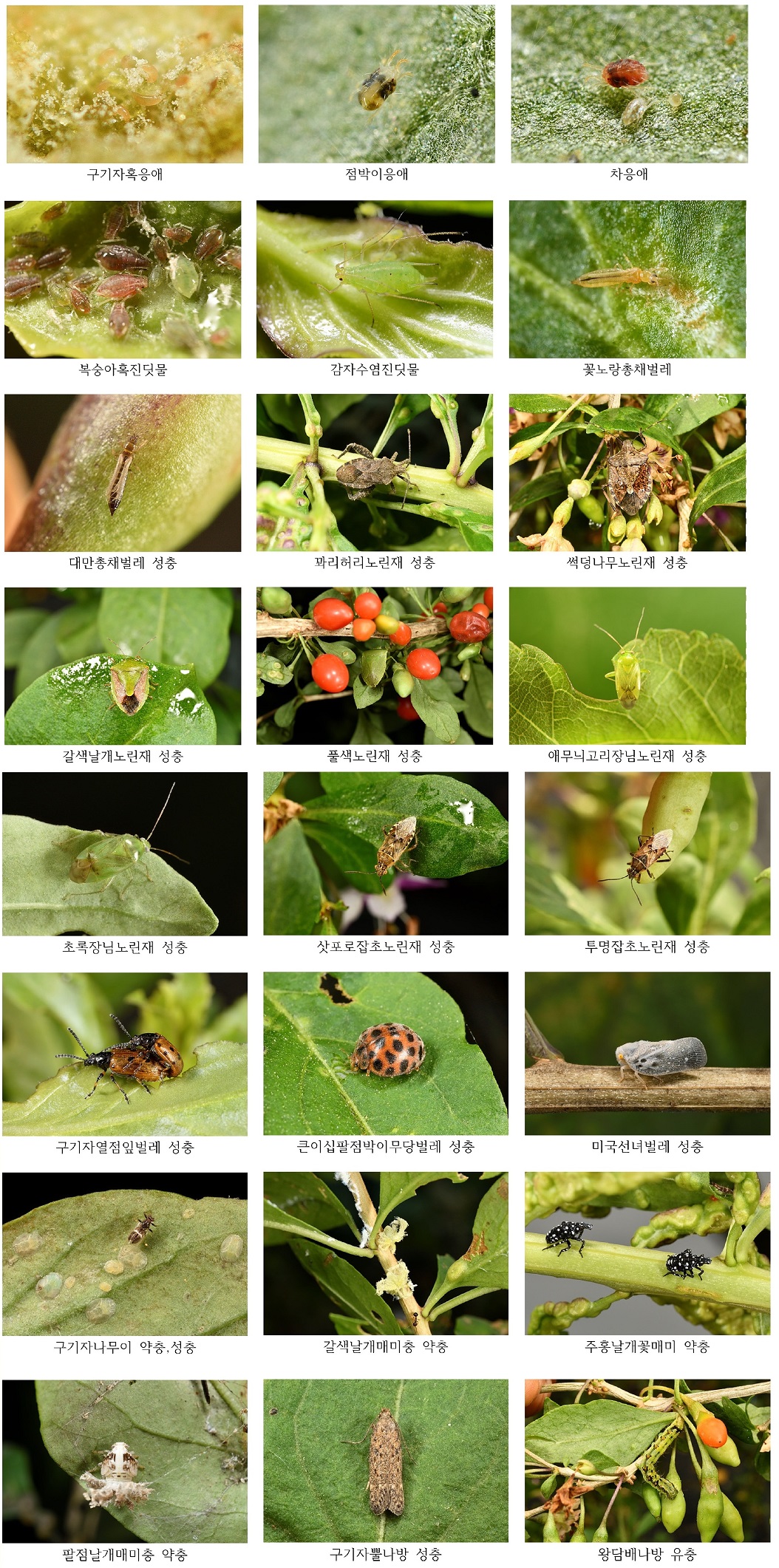
구기자에 발생하는 해충으로 총 6목 24과 47종을 확인하였다(Table 1). 이들 해충의 발생과 피해수준을 소(+), 중(++), 다(+++), 심(++++)으로 구분하였을 때 발생과 피해가 다(+++) 또는 심(++++)에 포함되는 해충으로는 갈색날개매미충, 구기자나무이, 미국선녀벌레, 꽈리허리노린재, 복숭아혹진딧물, 감자수염진딧물, 애모무늬고리장님노린재, 풀색노린재, 갈색날개노린재, 썩덩나무노린재, 알락수염노린재, 초록장님노린재, 삿포로잡초노린재, 투명잡초노린재, 구기자뿔나방, 도둑나방, 왕담배나방, 미국흰불나방, 열점박이잎벌레, 큰이십팔점박이무당벌레, 구기자혹응애, 꽃노랑총채벌레, 대만총채벌레, 주홍날개꽃매미 등 24종 이었고 이들 주요해충에 대한 사진은 Fig. 1과 같다. 노린재목 61.7%, 나비목 14.9%, 응애목 8.5%, 총채벌레목 6.3%, 병안목 4.2%로 노린재목이 대부분을 차지하였다.
방제효과 포장검정
발생초기 약제살포 방법으로 2020년 5종의 살충제에 대하여 충남지역 예산과 청양의 구기자 재배포장에서 구기자혹응애의 방제효과를 검정한 결과, azocyclotin WP에서 예산과 청양이 각각 92.4%와 93.2%의 높은 살비력을 보였을 뿐 다른 화학약제에서는 70% 이하의 낮은 살비력을 보였다(Table 3, 4).

Control effect of Eriophyes sp. on five acaricides in gojiberry field in Yesan region after 15 days of final treatment in the early occurrence of Eriophies sp.

Control effect of Eriophyes sp. on five acaricides in gojiberry field in Cheongyang region after 15 days of final treatment in the early occurrence of Eriophies sp.
구기자혹응애는 이듬해 잔재물, 낙엽, 가지의 조피 틈 속 등에서 월동 후 새싹이 돋아나는 4월 중순경부터 신초로 이동하여 곧바로 가해를 하고 혹을 형성하기 때문에 이미 혹을 형성한 이후에는 화학약제의 사용에도 살비효과가 떨어지는 문제점이 있다. 따라서 사전밀도를 조사하여 화학약제를 살포하는 것은 약제를 사용하는 방법적인 면에서 맞지 않는 기준일 수 있다. 이를 보완하기 위하여 두 번째 실험에서는 신초가 발생하기 전부터 1주 간격으로 2회 약제를 살포하는 방법을 선택하였다. 2020년에는 4월 20일 신초가 발생하였고 2021년에는 4월 19일 신초가 발생하여 거의 비슷한 시기임을 확인하였으며 구기자 신초 발생 전 약제 살포는 4월 12일 1차 살포하고 4월 19일 2차 살포하였다. 시험구 배치는 발생초기 약제살포 방법과 동일하였다.
구기자 신초 발생전 약제살포 방법으로 2020년에 사용한 5종 화학약제에 대하여 예산과 청양의 구기자 재배포장에서 구기자 혹응애의 방제효과를 검정한 결과, 예산의 경우 cyflumetofen SC와 azocyclotin WP가 각각 94.6%와 95.9%의 높은 살비력을 보였고 청양의 경우 각각 95.9%와 97.6%의 높은 살비력을 보였다. 나머지 약제들은 80% 이하의 낮은 살비력을 보였다(Table 5, 6).

Control effect of Eriophyes sp. on five acaricides in gojiberry field in Yesan region after 15 days of final treatment before the occurrence of Eriophies sp.

Control effect of Eriophyes sp. on five acaricides in gojiberry field in Cheongyang region after 15 days of final treatment before the occurrence of Eriophies sp.
Cyflumetofen SC는 2000년대 후반 살비제에 저항성을 가지는 많은 응애류 방제용 약제를 대신하여 사용이 가능할 정도로 효과가 좋았던 약제로 미토콘드리아의 전자 전달 기능을 억제하는 것으로 알려져 있다(Takahashi et al., 2012). 또한 잔효성이 길면서 유익한 절지동물과 비표적 유기체에 안전한 환경 안전성을 보이기 때문에 해충종합관리 프로그램이나 내성 관리 프로그램에 이상적일 수 있으며 응애류의 발육단계에 구애받지 않고 살비력을 보여준다 하였다. Acequinocyl SC는 응애의 미토콘드리아 호흡을 억제하는 작용기작을 가지며 점박이응애에 대한 저항성과 관련된 여러 기작들이 밝혀져 왔다(Choi et al., 2020; Fotoukkiaii et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2019). Azocyclotin WP는 산화적 인산화를 억제하여 ATP 형성을 방해하는 작용 기작을 가지며, 최근 pyridaben 저항성 관리를 위해 교호 살포가 가능한 살비제로 알려져 있다(van Leeuwen et al., 2010; Niu et al., 2022). Flufenoxuron DC는 peritrophic membrane 생성 세포의 키틴 합성을 방해하여 막의 비정상적 구성과 방어 기능의 소실을 일으키는 바이러스성 키틴합성 저해제로 개발되었고 주로 나비목 해충에 효과가 우수한 것으로 알려져 있는 곤충생장조절제(IGR)이다(Arakawa, 2001). Etoxazole SC는 1990년에 일본에서 처음개발된 살비제로 pyridaben과 마찬가지로 곤충의 키틴 생합성 저해를 일으키는 곤충생장조절제이다(Koo e t al., 2021; Dekeyser, 2005; Suzuki et al., 1989).
구기자를 가해하는 다른 응애류인 점박이응애 방제제로 등록된 살비제는 acequinocyl SC, etoxazole SC, flufenoxuron DC, cyflumetofen SC 이다. 이미 사용되어 온 이들 약제들 중 방제 효과가 가장 낮았던 acequinocyl SC와 etoxazole SC는 점박이응애에 대한 저항성 보고가 확인되었던 만큼 구기자혹응애에도 저항성을 유발했을 가능성이 높을 것으로 판단되었으며 이보다 등록이 늦게 되었던 cyflumetofen SC는 처리방법 개선으로 azocyclotin WP와 함께 구기자혹응애방제용으로 등록이 가능할 것으로 판단되어 이 두 약제를 구기자 혹응애 전용약제로의 등록을 적극 추천하는 바이다.
Acknowledgments
본 연구는 농촌진흥청 농업공동연구인 “자가제조 유기농업자재 및 천적의 과채류 현장적용 모델개발(PJ01558202022)” 수행중 과채류 등록 약제에 대한 응애류 살비효과 검정 중 얻어진 결과물로 본 과제의 지원을 받아 수행되었습니다.
이해상충관계
저자는 이해상충관계가 없음을 선언합니다.
References
- Agricultural Technology Research Center, 1994. Primary color medicinal crop pest illustration pp214.
-
Arakawa T, 2002. Promotion of nucleopolyhedrovirus infection in larvae of the silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) by flufenoxuron. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 37(1):7-11.
[https://doi.org/10.1303/aez.2002.7]

-
Choi J, Koo HN, Kim SI, Park B, Kim H, 2020. Target-site mutations and glutathione S-transferases are associated with acequinocyl and pyridaben resistance in the two-spotted spider mites, Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Insects 11(8):511.
[https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080511]

- Ehara S, Shinkaji N, 1996. Principles of plant acarology. Zenkoku Noson Kyoiku Kyokai, Tokyo pp. 419.
- Forestry Research Institute, 1995. List of Korean Tree Pests. Forestry Research report pp. 106 and 184.
-
Fotoukkiaii SM, Tan Z, Xue W, Wybouw N, Van Leeuwen T, 2020. Identification and characterization of new mutations in mitochondrial cytochrome b that confer resistance to bifenazate and acequinocyl in the spider mite Tetranychus urticae. Pest Manag. Sci. 76(3):1154-1163.
[https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5628]

- Kim CH, 1965. The injured conditions of Eriophyes kuko Kishida. Korea J. of Appl. Entomol. 4:65-66.
- Kim CH, 1968. Some biological notes on Eriophyes kuko Kishida. (1) Its biology and life history. Korea J. of Appl. Entomol. 5_6:59-63.
- Kim CM, 1989. A systematic study on the superfamily Eriophyoidea (Acari: Eriophyoidea) in Korea. Thesis of M. Sc. Seoul National University pp. 37.
- Kim CH, Sigenobu K, So IY, 1972. Studies on Eriophyes kuko Kishida and its galls. IV. Studies on the growing mite gall under light and electron microscopes. Applied Microscopy. 2:17-31.
-
Kim SI, Koo HN, Choi Y, Park B, Kim HK, et al., 2019. Acequinocyl resistance associated with I256V and N321S mutations in the two-spotted spider mite (Acari: Tetranychidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 112(2):835-841.
[https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/toy404]

- Lee SG, Yoo JK, Choi IH, Park KH, Lee JO, 1994. Damage of Lycium chinenes mill by Eriophys macrodonis keifer and its chemical controls. RDA J. Agri. Sci. 36(1):362-365.
- Lee WK, 2006. Eriophyid mites associated with Lycium chineses Mill in Korea. Kor. J. of Soil Zool. 11(1-2):13-15.
-
Niu JZ, Liu GY, Dou W, Wang JJ, 2011. Susceptibility and activity of glutathione S-transferases in nine field populations of Panonychus citris (Acari: Tetranychidae) to pyridaben and azocyclotin. Florida Entomol. Soc. 94(2):321-329.
[https://doi.org/10.1653/024.094.0227]

- Park DG, In MS, Jang YD, 1993. Ecology and variety resistance test of Eriophyes kuko Kishida. CNARES J. Agri. Sci. pp. 309-311.
- SAS Institute, 2011. SAS/STAT user’s guide, version 9.3. SAS Institute, Cary, NC.
-
Takahashi N, Nakagawa H, Sasama Y, Ikemi N, 2012. Development of a new acaricide, cyflumetofen. J. of Pesti. Sci. Japan. J12:03.
[https://doi.org/10.1584/jpestics.J12-03]

-
Van Leeuwen T, Vontas J, Tsakarakou A, Dermauw W, Tirry L, 2010. Acaricide resistance mechanisms in the two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae and other important Acari: A review. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 40(8):563-572.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.05.008]

YongSeok Choi, Bio-Environmental Division, Chungnam Agricultural Research and Extension Services, Researcher, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4822-9918
DeogGee Park, Department of Botanical Medicine, Suncheon National University, Researcher
InSu Hwang and KyungJoo Lee, Bio-Environmental Division, Chungnam Agricultural Research and Extension Services, Asistant
SeongWon Yoon, GunWoo Lee, Bio-Environmental Division, Chungnam Agricultural Research and Extension Services, Researcher
SeungWan Son, Gojiberry Research Institute, Chungnam Agricultural Research and Extension Services, Researcher
JeongIll Joo, Bio-Environmental Division, Chungnam Agricultural Research and Extension Services, Director
