감자 품종 “역강” 중심공동 억제를 위한 처리기술
초록
새로운 감자 품종 “역강”은 역병에 저항성이 있지만, 중심공동이 문제가 된다. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 감자 재식간격을 20, 25, 30cm로 파종하는 실험과 boric acid, CaCl2, boric acid + CaCl2, sulfur fertilizer, diniconazole SC, prohexadione-calcium SC 처리하는 실험을 수행하였다. 재식거리에 따른 실험을 고랭지에서 수행한 결과 중심공동 발생률은 20, 25, 30 cm 간격에서 각각 15.7%, 13.7%, 18.4%로 나타났다. 처리물질에 따른 실험은 평난지실험에서 중심공동 발생률은 무처리에서 15.6%였지만, diniconazole SC처리에서 1.7% 발생하여 무처리 대비 89.1% 발생을 억제하여 무처리와 통계적 유의성있는 차이가 있었다. 고랭지 실험 기준 중심공동 발생률은 무처리에서 24.0%였으며, prohexadione-calcium SC처리에서 14.0%로 처리간 가장 낮은 발생률을 나타냈다. 위 결과를 통해 감자 파종시 재식간격은 25 cm로 하고, diniconazole SC나 prohexadione-calcium SC를 적절히 사용시 감자 품종 “역강” 재배 기간 동안 중심공동을 개선할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
Abstract
The new potato variety “Yeokgang” is resistant to late blight, but the hollow heart is a problem. In order to improve this, experiment of sowing of potatoes at 20, 25, and 30 cm plant spacing and experiment of treating of boric acid, CaCl2, boric acid + CaCl2, sulfur fertilizer, diniconazole SC, and prohexadione-calcium SC were conducted. The experiment according to the plant spacings was conducted in the highland field, and the hollow heart incidence was 15.7%, 13.7%, and 18.4% at 20 cm, 25 cm, and 30 cm plant spacings, respectively. In the experiment according to the treatment, the ratio of hollow heart in the lowland field was 15.6% in the control, but it was the lowest at 1.7% in the diniconazole SC foliar spray of 10 days and 20 days after flowering, showing a statistically significant difference from other treatments. The ratio of hollow heart in the highland was 24.0% in the control and 14.0% in the prohexadione-calcium SC foliar spraying at 50 days and 60 days after seeding, which was the lowest among the examined various treatments. According to the experiment results, appropriate potato plant spacing, 25 cm and as well as foliar spraying of diniconazole SC and prohexadione-calcium SC can expect improvement the incidence of hollow heart of “Yeokgang” potato during cultivation period.
Keywords:
Diniconazole, Hollow heart, Plant spacing, Yeokgang potato키워드:
감자, 중심공동, 재식거리, 역강서 론
감자(Solanum tuberosum L.)는 전 세계적으로 재배되고 있는 주요 식량작물로 단위면적당 생산성이 높고 환경적응성이 뛰어나 주식 및 가공용 식재료로 널리 이용되고 있다.
감자 재배 중 발생하는 생리장해에는 주로 내부 갈색반점(internal brown spot), 흑색심부(black heart), 이차생장(second growth), 중심공동(hollow heart) 등이 있다(O'Brien and Rich, 1976). 그 중에서도 중심공동은 주로 크기가 큰 괴경에서 발생하며 품종 중 “대서”와 같은 가공용 품종에서 많이 관찰되며, 괴경 절단 시 공동이 생긴 부위는 흰색 또는 엷은 황갈색을 띄며 별모양이나 불규칙한 모양의 구멍이 발생한다. 생리장해로 감염 미생물에 의해 발생하는 것이 아니므로 전염되지 않지만 품질을 크게 저하시키므로 심각한 손실을 초래한다. 또한 이 증상은 괴경을 절단하여 관찰하기 전에는 외관상으로 판별되지 않기 때문에 발견이 어렵다(Atanasoff, 1926; Krantz and Inan, 1942). 중심공동은 품종 선택, 파종밀도, 토양 비옥도, 관개 및 해충 관리를 포함한 다양한 영향을 받는다. 제초작업의 생력화와 토양유실을 막기 위하여 흑색필름 멀칭재배의 경우 일반재배보다 중심공동의 발생이 증가한다고 한다(Kim et al., 1997a). 중심공동 발생은 직경이 수 mm에서 최대 2 cm 이상일 수 있으며 전체 감자가 거의 공동이 되는 경우도 있다(Bussan, 2007).
중심공동 발생은 품종 및 재배 장소, 시기에 따라 차이를 보인다(Rex and Mazza, 1989). 특히 고랭지 여름 재배시 대발생으로 가공원료의 확보가 어려워져 일부 가공제품 생산라인에서의 가동율을 감소시키는 원인이 된다(Kim et al, 1997b). 이러한 문제점을 개선하기 위해 잎 제거와 차광에 따른 실험(Keantz and Lana, 1942), 감자 괴경 크기와 수확시기에 따른 실험(Nelson and Thoreson, 1986), X선 기계와 같이 중심공동과를 비파괴적으로 감지하기 위한 기술이 일부 개발되었다(Finney and Norris, 1978). Nelson(1970)은 재식시기와 간격 및 처리물질에 따른 실험으로 조기 파종과 칼륨비료 사용시 중심공동이 어느정도 감소되는 것을 보고한 바가 있다.
국내에서도 중심공동 개선을 위한 연구로 멀칭재료에 따른 중심공동 발생률, 재식밀도와 질소비료가 중심공동에 미치는 영향과 질소, 칼슘 시비와 재식거리, 복토깊이에 따른 중심공동 발생 등이 보고되었다(Kim et al., 1997a, 1997b; Yang et al., 2001).
감자 품종 “역강”은 페루에서 도입된 역병저항성 CIP2424A계통을 모본으로하고 국내 육성품종인 고전분 중만생종인 오륜(Oryun)을 부본으로 하여 2011년 인공교배를 실시하여 육성된 품종이다(Maeng et al., 2015). 이 품종은 생산력 검정시험과 지역적응시험 및 특성검정을 수행하여 수량성이 우수하고 특히 역병에 진정 저항성을 가지므로 품종명을 ‘역강(Yeokgang)’으로 명명하였다(Gwares, 2019). 역강 품종은 중만생종으로 괴경모양은 원형이며 표피색은 황색이다. 점질형 감자이나 전분함량이 높으며, 역병에 고도의 저항성을 가진 품종으로 친환경재배가 가능하다. 그러나 품종 특성상 중심공동과가 빈번히 발생하여 품질저하 등의 문제가 나타난다.
따라서 본 연구는 감자 품종 “역강”의 중심공동 문제를 개선하기 위한 연구로 재식거리와 처리물질에 따른 개선 효과를 비교 조사하였다.
재료 및 방법
실험재료
실험을 진행하기 위한 공시품종으로 감자 역병에 저항성인 “역강(Yeokgang)”을 사용하였다. 공시재료는 2020년과 2021년 강릉시 왕산면에 위치한 해발 720m 고랭지에서 수확한 종서를 4°C 저온저장고에 보관과정을 거친 후 휴면타파 하여 실험에 사용하였다.
재식거리에 따른 중심공동 발생조사
실험은 2021년 진행하였으며 평균 90일~100일이 소요되는 감자재배와 비슷하게 파종부터 수확까지 약 120일 정도 소요되었다. 실험포장은 강원도 강릉시 왕산면 고랭지에 위치한 사양토에서 멀칭은 하지 않은 상태로 재배하였다. 재식거리는 20, 25, 30 cm 간격으로 설정하였으며, 처리구 당 20주씩 파종하고 시험구 배치는 난괴법으로 3반복으로 진행하였다.
처리물질에 따른 중심공동 억제효과
본 실험은 2022년 진행하였으며 재식거리에 따른 실험과 동일하게 파종부터 수확까지 약 120일 정도 소요되었으며, 포장지로 고랭지는 강릉시 왕산면 대기리 포장지를 사용하였고, 평난지는 강릉시에 위치한 강릉원주대학교 부속농장 내 포장을 사용하였다. 파종을 위한 재식거리는 재식거리에 따른 중심공동 발생 실험 결과를 참고하여 고랭지와 평난지 모두 동일하게 25 cm로 설정하여 실험하였다.
처리물질은 boric acid (Daejung), CaCl2 (Daejung), boric acid + CaCl2 (Daejung), sulfur fertilizer (Hsulphur), diniconazole SC (5%), prohexadione-calcium SC (20%)로 총 7처리로 수행하였다. 시비 방법으로 sulfur fertilizer는 파종 전 전면처리 하였으며 boric acid, CaCl2, boric acid + CaCl2, diniconazole SC는 개화 10일 후 1회 처리와 20일 후 2회 처리로 엽면살포 하였다. Prohexadione-calcium SC는 파종 50일 후 1회 처리와 60일 후 2차 처리로 엽면살포 하였다. 실험은 난괴법 3반복으로 하였고 한 처리구 당 20주씩 파종하였다(Table 1).
조사항목 및 통계분석
재식거리와 처리물질에 따른 두 실험 모두 동일하게 각 처리구별 수량지표인 괴경수, 괴경중, 상서율과 중심공동 발생률을 조사하였으며, 실험으로 얻어진 결과의 통계분석은 SAS system (SAS Institute Inc. Cary NC 27513, USA)을 이용하여 분산분석(ANOVA)을 하였으며 Duncan의 다중검정(DMRT)를 이용하여 P≤ 0.05 수준에서 각 처리간의 유의성을 검증하였다. 중심공동 발생률(%) 아래수식으로 산출하였다.
중심공동 발생률(%) = 발병 괴경 수/조사 괴경 수 × 100
결과 및 고찰
재식거리에 따른 중심공동 발생
재식거리에 따른 중심공동 발생은 Table 2에 나타난 결과와 같다. 괴경중은 재식간격 25 cm에서 평균 115.3 g으로 조사한 재식간격 중 가장 높았으나 통계적 차이는 없었고, 괴경수는 30 cm 간격에서 6 .2개로 25 cm에서 5.9와 유의적인 차이는 없었으나 20 cm에서 5.3개와는 통계적으로 유의하게 괴경수가 많았다. 상서율은 20 cm 재식간격에서 81.5%로 나타나서 괴경수는 다른 처리구에 비해 적은 반면 상서율은 높았으나 재식 간격 간에 유의적인 차이는 없었다. 중심공동 발생률은 25 cm에서 13.7%로 가장 낮았지만 통계적 유의성은 없었다. Yang et al. (2001)은 가공용 감자품종인 “대서” 품종의 평난지와 고랭지 포장 재배에서 관행재식거리(75 × 25 cm)보다 밀식 재식거리(75 × 20, 75 × 15 cm)에서 중심공동 발생이 적었고 복토 깊이를 10 cm에서 20 cm로 깊게 할 때 감소하였다고 보고했다.

Effect of planting distance on tuber weight, tuber number per plant, ratio of marketable tuber, and ratio of hollow heart
재식거리에 따른 중심공동 개선효과는 25 cm를 기준으로 재식거리가 넓어짐에 따라 중심공동 발생률이 높아졌고 재식간격 20 cm와 비교하여 중심공동 발생률에서 25 cm 재식간격은 유의적인 차이는 없었다. 그러나 20 cm 재식간격은 식물체 당 괴경수가 현저히 줄어드는 것을 확인하였다. 따라서 종합적인 측면에서 보았을 때 25 cm의 재식거리에서 감자 “역강”의 중심공동 문제가 효과적으로 개선될 수 있을 것으로 사료된다.
처리물질에 따른 중심공동 억제효과
평난지에서 수행한 처리물질에 따른 효과는 괴경중은 101.8-120.5 g으로 무처리에서 120.5 g으로 가장 높은 수치를 보였으나 처리간에 유의성은 없었고 괴경수도 4.0~4.6개로 처리효과가 없었다. 상서율은 sulfur fertilizer에서 81.9%로 수치상 가장 높았으나 다른 수량지수와 마찬가지로 처리간 유의성은 없었다(Table 3, Fig. 1) 중심공동 발생률은 diniconazole SC을 개화 10과 20일에 2번 살포한 처리구에서 1.7%로 무처리 발생률 15.6%와 비교하여 89.1% 억제하여 뚜렷한 효과를 나타냈다(Table 3, Fig. 1) 다른 처리구(boric acid, CaCl2, boric acid + CaCl2, sulfur fertilizer)도 무처리 대비 중심공동을 억제하였지만 통계적 유의성은 없었다.

Effect of treatments on tuber weight, tuber number per plant, ratio of marketable tuber, and ratio of hollow heart in lowland
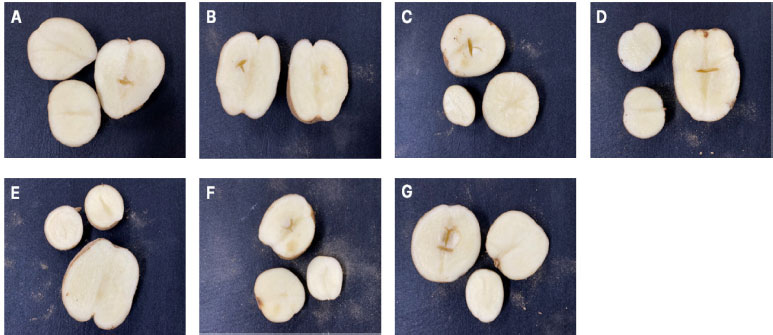
Hollow heart symptoms by treatments in lowland. A: Boric acid, B: CaCl2, C: Boric acid + CaCl2, D: Sulfur fertilizer, E: Diniconazole SC, F: Prohexadione-calcium SC, G: Control.
고랭지에서 수행한 처리물질에 따른 수량지수 괴경중은 89.7-101.1 g으로 무처리에서 101.1 g으로 가장 높은 수치를 보였으나 처리간에 통계적 유의성은 없었다(Table 4, Fig. 2). 괴경수는 처리물질 간 차이가 없이 6.2~6.8개로 나타났다. 평난지 4.0-4.6개와 비교하였을 때 고랭지에서 많은 괴경수를 나타내는 것을 보았을 때 고랭지가 감자 재배에 유리하다는 것을 알 수 있다. 상서율도 75.2-72.2%로 처리간에 유의적인 차이가 없었다. 평난지의 무처리구에서 중심공동 발생률은 1 5.6 %인 반면 고랭지의 무처리구에서 24.0%로 고랭지 포장에서 중심공동 발생률이 높게 나타났다. 중심공동 발생은 괴경 비대기에 고온 및 건조 환경으로 인해 칼슘이 흡수되지 않아 발생하는 것으로 알려졌다(Rex and Mazza, 1989). 특히 고랭지 여름 재배에서 평난지 봄재배보다 중심공동 발생 환경이 조성되기 때문에 중심공동을 억제하는 기술이 평난지 봄재배보다 더욱 필요하다. 고랭지 실험에서 중심공동 발생률은 prohexadione-calcium SC를 파종 50일과 60일에 2회 엽면처리하는 처리구에서 14.0%로 무처리 24.0%와 비교하여 41.7% 억제효과가 있었지만 전처리구 간에는 통계적 유의성은 없었다.

Effect of treatments on tuber weight, tuber number per plant, ratio of marketable tuber, and ratio of hollow heart in highland
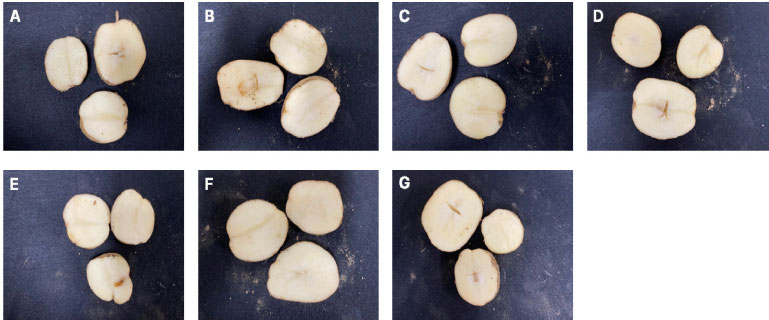
Hollow heart symptoms by treatments in highland. A: Boric acid, B: CaCl2, C: Boric acid + CaCl2, D: Sulfur fertilizer, E: Diniconazole SC, F: Prohexadione-calcium SC, G: Control.
처리물질에 따른 중심공동 개선효과에서 평난지 기준 diniconazole SC, 고랭지 기준 prohexadione-calcium SC 처리에서 중심공동 발생이 개선되었다. Diniconazole은 triazole계 살균제로 국내에서 과수에 발생하는 병 및 채소에 발생하는 병을 방제하는 살균제이다. 하지만 이 살균제는 부작용으로 식물의 지베렐린의 생성을 억제하므로 작물생육 억제제로도 널리 이용되고 있다(Kim et al., 2016; Sun et al., 2002; Yeoung et al., 2005). 고랭지 여름배추 재배는 고온다습한 환경이며 여름철 장마기에 재배하기 때문에 일조부족으로 배추가 도장하여 품질이 저하된다. Diniconazole은 여름배추 재배 중 엽면살포하면 도장을 억제하며 엽수가 증가하며 엽록소 함량이 증가하며 세포를 치밀하게 하여 품질을 향상시킨다(Sun et al., 2002; Yeoung et al., 2005). Kim et al. (2016)은 토마토 접목묘의 하계 육묘 시 도장 억제를 통한 건전한 묘를 생산하고자 diniconazole를 이용할 때에는 10 mg L-1 이하의 농도로 하여 사용하는 것이 적합하다고 보고하였다.
감자도 diniconazole을 처리하면 배추와 마찬가지로 도장을 억제하며 줄기가 단단해지는 효과가 있다(본문에 미보고). Prohexadione-calcium도 생장조절제로 등록되어있는 물질이다(US EPA, 2000). 실험에 앞서 생육억제 효과로 인한 괴경 수량감소를 예상하였지만 실험결과 수량감소는 되지 않는 선에서 중심공동은 억제되는 결과를 얻을 수 있었다. 이에 따라 diniconazole SC와 prohexadione-calcium SC를 적절히 사용시 감자품종 “역강”의 중심공동 문제가 효과적으로 개선할 수 있을 것으로 사료된다.
Acknowledgments
본 연구는 농촌진흥청 공동연구사업(과제번호: PJ01560603)의 지원에 의해 이루어진 “고위도 지역 적응 감자 수확 후 관리 및 이용성 증진 연구” 과제로 수행되었습니다.
이해상충관계
저자는 이해상충관계가 없음을 선언합니다.
References
- Atanasoff D, 1926. Sprain or internal brown spot of potatoes. Phytopathology 16:711-722.
-
Bussan AJ, 2007. The canon of potato science: 45. Brown centre and hollow heart. Potato Res. 50(3):395-398.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-008-9087-0]

-
Finney EE, Norris KH, 1978. X-ray scans for detecting hollow heart in potatoes. Ame. Potato J. 55:95-105.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02852096]

- Gangwon-do Agricultural Research & Extensions Services, 2019. Potatoes resistant to late blight “Yeokgang”. https://www.ares.gangwon.kr/gwares/know_how/research/application_data?articleSeq=32214, .
-
Keantz FA, Lana EP, 1942. Incidence of hollow heart in potatoes as influenced by removal of foliage and shading. Ame. Potato J. 19(7):144-149.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02850096]

-
Kim HC, Cho YH, Ku YG, Hwang SJ, Bae JH, 2016. Growth characteristics of grafted tomato seedlings following treatment with various concentrations of diniconazole during the summer growth season. Hort. Sci. Technol. 34(2): 249-256. (In Korean)
[https://doi.org/10.12972/kjhst.20160026]

- Kim HJ, Kim SY, Shin KY, Yang SJ, 1997a. Effects of mulching materials on the hollow heart and internal brown spot in potato tubers. J. Kor. Soc. Hort. Sci. 38(1):6-8.
- Kim HJ, Kim SY, Shin KY, Yang SJ, 1997b. Effects of planting density and nitrogen fertilizer level on the occurrence of hollow heart and internal brown spot of processing potato tubers. J. Kor. Soc. Hort. Sci. 38(2):107-110.
-
Maeng JH, Ahn SY, Choi SJ, Kwon SB, Kim BS, 2015. A mid-late maturing potato variety ‘oryun’ with high starch. Kor. J. Breed. Sci. 47(1):92-95. (In Korean)
[https://doi.org/10.9787/KJBS.2015.47.1.092]

-
Nelson DC, Thoreson MC, 1986. Relationships between tuber size and time of harvest to hollow heart initiation in dry land Norgold Russet potatoes. Ame. Potato J. 63:155-161.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02853539]

-
Nelson DC, 1970. Effect of planting date, spacing, and potassium on hollow heart in Norgold Russet potatoes. Ame. Potato J. 47(4):130-135.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02871093]

- O'Brien MJ, Rich AE, 1976. Potato diseases (No. 474). US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service.
-
Rex BL, Mazza G, 1989. Cause, control and detection of hollow heart in potatoes: A review. Ame. Potato J. 66(3): 165-183.
[https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02853679]

- Sun SY, Jeon JY, Yeoung YR, Kim BS, 2002. Application of diniconazole for growth inhibition of Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinsis Rupr.) for summer production in alpine region. J. Kor. Soc. Hort. Sci. 43(3):280-284. (In Korean)
- US EPA. 2000. Pesticides - Fact Sheet for Prohexadione Calcium. https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/registration/fs_PC-112600_26-Apr-00.pdf, .
- Yang SJ, Ku OS, Lim HT, 2001. Effects of cultivation methods on the occurrence of internal brown spot and hollow heart in potato tubers. J. Kor. Soc. Hort. Sci. 42(1):75-77. (In Korean)
- Yeoung YR, Yoon CS, Kim BS, 2005. Influence of fungicide diniconazole in Chinese cabbage on leaf morphology and chlorophyll concentration. J. Kor. Soc. Hort. Sci. 46(1):13-17.
Nam-sook Kim, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Master student, Investigation, Data analysis, Writing
Heon-seop Won, Potato Experiment Station, Gangwondo Agricultural Research and Extension Services, Researcher, Investigation, Data analysis, Writing
Se-Hwi Gwon, Gangneung-Wonju National University, PhD student, Investigation, Data analysis, Writing
Sae-jin Hong, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Professor, ORCID https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2602-0192, Bioassay experiment, Data analysis
Byung-sup Kim, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Professor, ORCID https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5247-6658, Research design, Draft review, Information collection, Writing
